Figure 6.
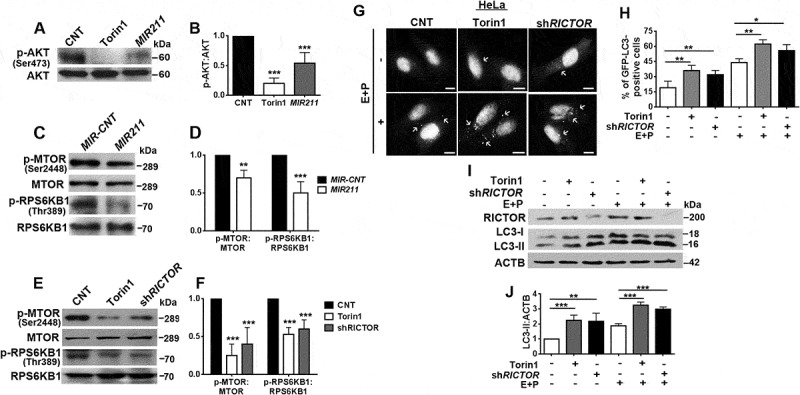
MIR211 regulated the MTORC1 pathway through RICTOR. (a) MTORC2-mediated AKT Ser473 phosphorylation was decreased in HeLa cells overexpressing MIR211. Torin1 was used as a positive control. (b) Graph depicting quantification of p-AKT:AKT ratios in the experimental set-up shown in A (mean± SD, n = 3 independent experiments, ***p < 0.01). (c) MTOR phospho-Ser2448 (p-MTOR) and RPS6KB1 phospho-Thr389 levels were decreased following MIR211 overexpression in HeLa cells. (d) Graph depicting quantification of p-MTOR:MTOR and p-RPS6KB1:RPS6KB1 ratios in the experimental set-up shown in C (mean± SD, n = 3 independent experiments, ***p < 0.01, **< 0.03). (e) Knockdown of RICTOR by shRNA (shRICTOR) decreased p-MTOR and p-RPS6KB1 levels. Torin1, positive control. (f) Graph depicting quantification of p-MTOR:MTOR and p-RPS6KB1:RPS6KB1 ratios in the experimental set-up shown in E (mean± SD, n = 3 independent experiments, ***p < 0.01). (g) Knockdown of RICTOR increased GFP-LC3 dot formation. Torin1, positive control. E + P, E64D and pepstatin A. Scale bar: 10 µm. (h) Quantitative analysis of GFP-LC3 dots in the experimental set-up shown in G (mean± SD of n = 3 independent experiments, **p < 0.03, *p < 0.05). (i) Immunoblots of LC3-II formation following knockdown of RICTOR. Torin1, positive control. (j) Graph depicting quantification of LC3B:ACTB ratios in the experimental set-up shown in I (mean± SD, n = 3 independent experiments, ***p < 0.01, **p < 0.03).
