Figure 5. DdcP and CtpA are membrane anchored with extracellular protease domains.
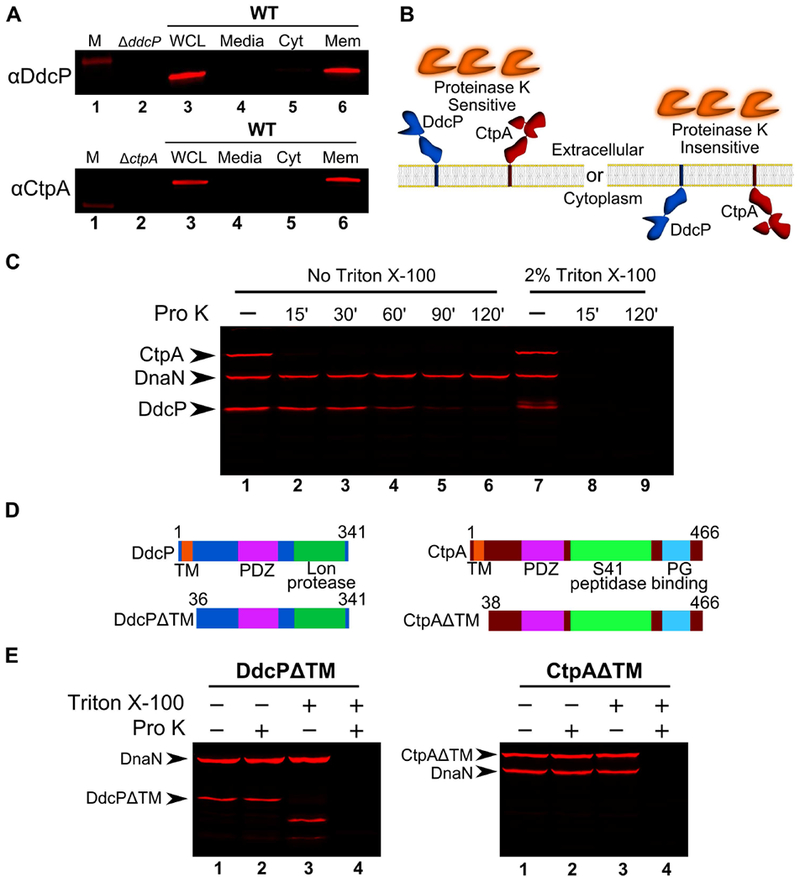
(A) Subcellular fractionation followed by Western blot analysis of WT (PY79) lysates using DdcP and CtpA antiserum (M, molecular weight standard, WCL, whole cell lysates; Media, precipitated media proteins; Cyt, cytosolic fraction; Mem, membrane fraction). (B) Competing models for membrane topology of DdcP and CtpA tested with proteinase K sensitivity assay. (C) Proteinase K sensitivity assay followed by Western blot detection of DdcP, CtpA, and DnaN with antiserum. Samples were treated with lysozyme to generate protoplasts and incubated with proteinase K for the indicated time (lanes 1-6), or the samples were incubated with lysozyme and Triton X-100 to disrupt the plasma membrane and incubated with proteinase K for the indicated time (lanes 7-9). (D) Schematics depicting the DdcPΔTM (left) and CtpAΔTM (right) in which the transmembrane domain was deleted. (E) Proteinase K sensitivity assay followed by Western blot analysis of strains expressing DdcPΔTM (left, PEB719) or CtpAΔTM (right, PEB772) performed as in panel C using a 2 hour incubation with proteinase K.
