Figure 3. Impact of E.coli (1×106 CFU/0.1mL/kg) in the spleen of male and female neonates 8- and 24-hours following infection.
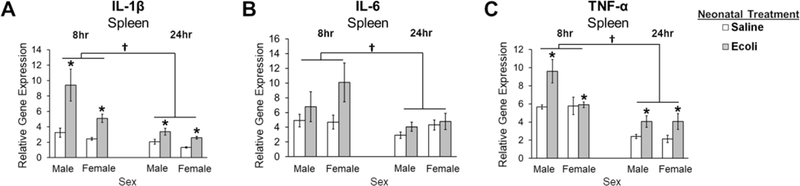
(A) Relative gene expression of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β is significantly increased in males and females following neonatal infection at both time points, but is significantly decreased at 24 hours post-infection compared to 8 hours. (B) Relative gene expression of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 is not significantly affected by neonatal infection and is significantly lower at 24 hours post-infection compared to 8 hours in males and females. (C) Relative gene expression of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α is increased in males and females following neonatal infection at both time points, but is significantly decreased at 24 hours post-infection compared to 8 hours. Error bars represent ±SEM. *p < .05 represents the main effect of Neonatal Treatment.†p < 0.05 represents the main effect of Time.
