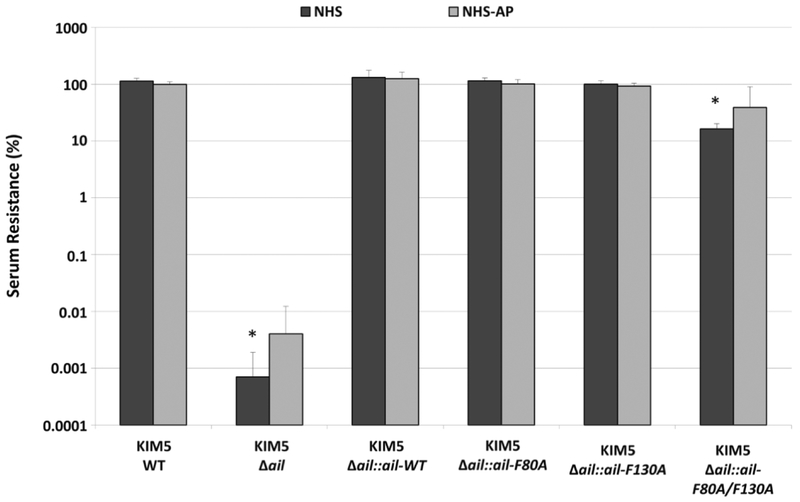
Figure 1. Killing of Y. pestis Δail by human serum is mediated by the alternative pathway of complement.
~7.5 × 105 CFU of mid-log cultures of Y. pestis strains containing wild-type Ail, a chromosomal deletion of ail (Δail), or chromosomal ail recombinants were treated with 80% NHS, 80% HIS (Heat-inactivated serum), or 80% NHS-AP (NHS treated with 5mM EGTA and 10mM MgCl2 to inactivate CP/LP) for one hour at 37°C. Surviving bacteria were plated and enumerated by colony counting. Percent serum resistance was calculated as the number of surviving colonies in NHS/HIS or NHS-AP/HIS x 100 and is displayed on a logarithmic scale. Strains were tested a minimum of 3 times for each condition in separate experiments. Significance was determined using the two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. *, p-value < 0.05 when compared to the parental KIM5 wild-type (WT) strain in the same serum condition.