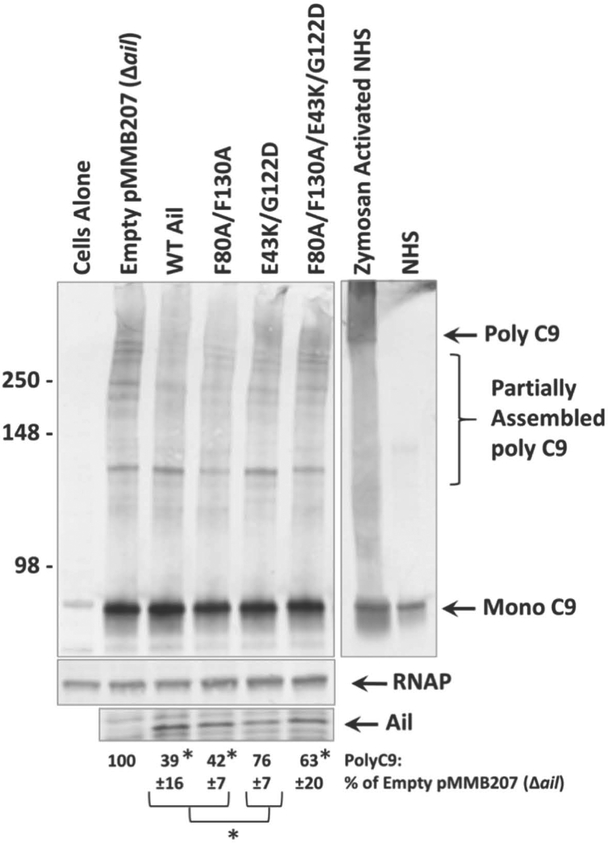
Figure 6. Membrane-association of polymerized C9 is increased in strains lacking ail or containing multiple mutations to extracellular loops.
Overnight cultures grown in the presence of 100μM IPTG (to induce Ail expression) were mixed with 50% NHS to a final OD620 = 0.25. Mixtures were shaken vigorously at 37°C for 30 minutes. Samples were centrifuged, cell pellets were washed, and subjected to Western blotting under non-reducing conditions using an anti-C9 polyclonal antibody. Western blot is one representative of at least three independent experiments. Ail expression was determined by Coomassie staining and is shown beneath the blot. Molecular weight markers are indicated on the left of the blot. Cells alone lane represents Y. pestis in the absence of NHS. Zymosan activated NHS is a positive control for the formation of polymerized C9 compared to NHS alone (monomeric C9). Quantification of band intensity from at least 3 independent experiments was performed using ImageJ software (NIH). Intensity of bands corresponding to C9 polymerization is shown as a percentage of the Δail mutant (a strain with no ability to inhibit C9 polymerization), which was normalized to 100%. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. *, p-value < 0.05 when compared to a strain expressing wild-type Ail.