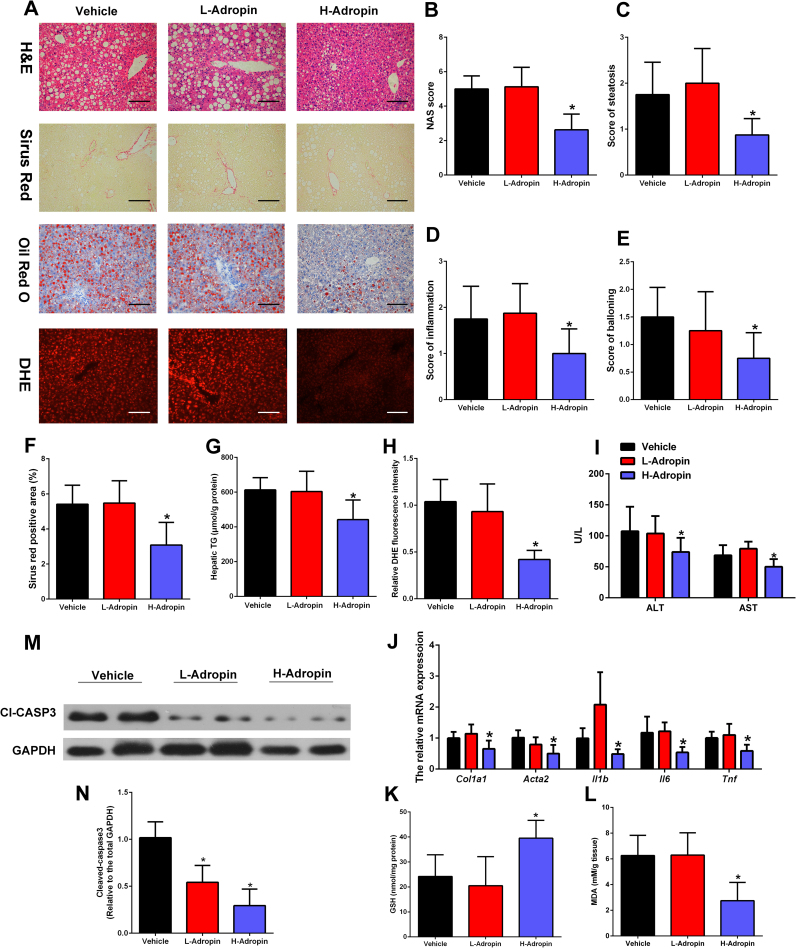
Fig. 4.
The bioactive adropin peptide ameliorated the liver injury in MCD-fed mice. C57BL/6 J mice were fed an MCD for four weeks and administered intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of vehicle, low-dose adropin (34−76) (50 nmol/kg/i.p.), or high-dose adropin (500 nmol/kg/i.p.) for one week. (A) Representative liver histology (H&E staining, Sirius Red, Oil Red O and DHE staining) (magnification, ×200), scale bar: 200 µm. (B-E) Hepatic histological analysis of H&E staining. (F) Quantitative analysis of Sirius Red staining. (G) Hepatic TG contents. (H) Quantitative analysis of DHE staining. (I) Serum ALT and AST levels. (J) The mRNA expression of Col1a1, Acta2, Il1b, Il-6 and Tnf in the liver. (K) The liver MDA levels. (L) The liver GSH levels. (M-N) Cleaved caspase-3 expression of total liver lysates. (H, J, N) Vehicle control group was set as 1. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 8, * P < 0.05 versus control group.