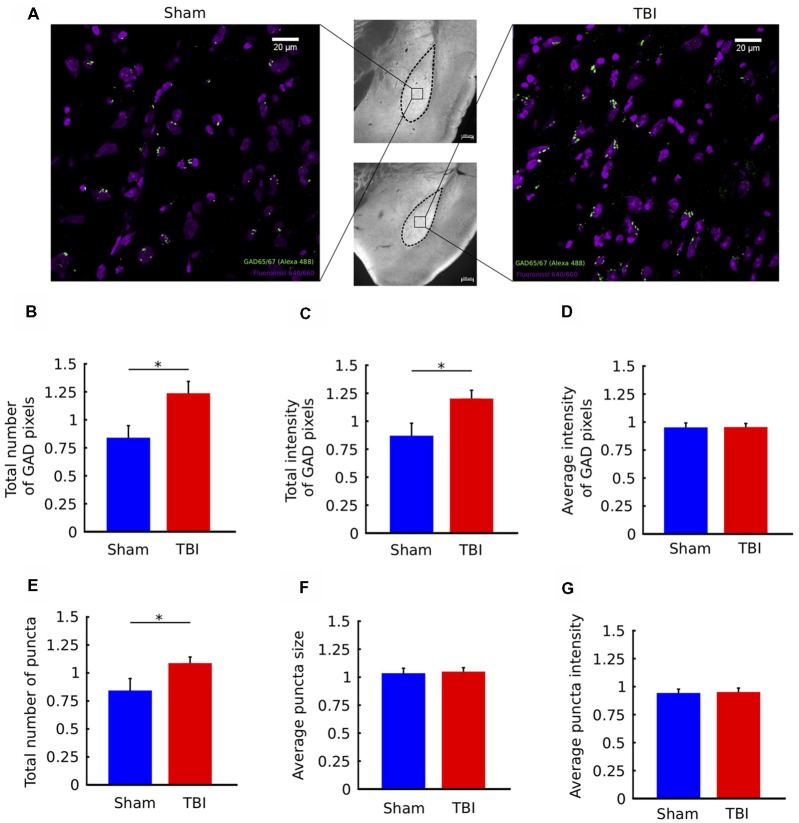
Figure 4.
TBI is associated with upregulation of GAD immunostaining in the ipsilateral amygdala. (A) Middle column: 10× images of histological sections from a sham animal (top) and TBI animal (bottom). Left/Right columns: 63× views of the indicated portions of the sections. Fluoro Nissl staining in purple and GAD65/67 staining in green. (B–G) Quantification of GAD65/67 expression in the ipsilateral and contralateral BLA in four sections per animal. Metrics in (B–G) are reported as ratios of ipsilateral to contralateral values for each animal. In injured animals, there was a significant increase in the total number of GAD pixels (B) and the total intensity of GAD pixels (C), but not the average intensity of GAD pixels (D). In addition, there was an increase in the total number of GAD “puncta” (clusters of contiguous GAD pixels (E), but not in the average size of puncta (F) or average intensity of puncta (G). All bar graphs show mean ± SEM of data from n = 10 mice in the TBI condition and n = 10 mice in the sham condition after removal of outliers (“Materials and Methods” section); the number of outliers did not exceed two mice for any; *p < 0.05 (two-tailed t-test).