Figure 7.
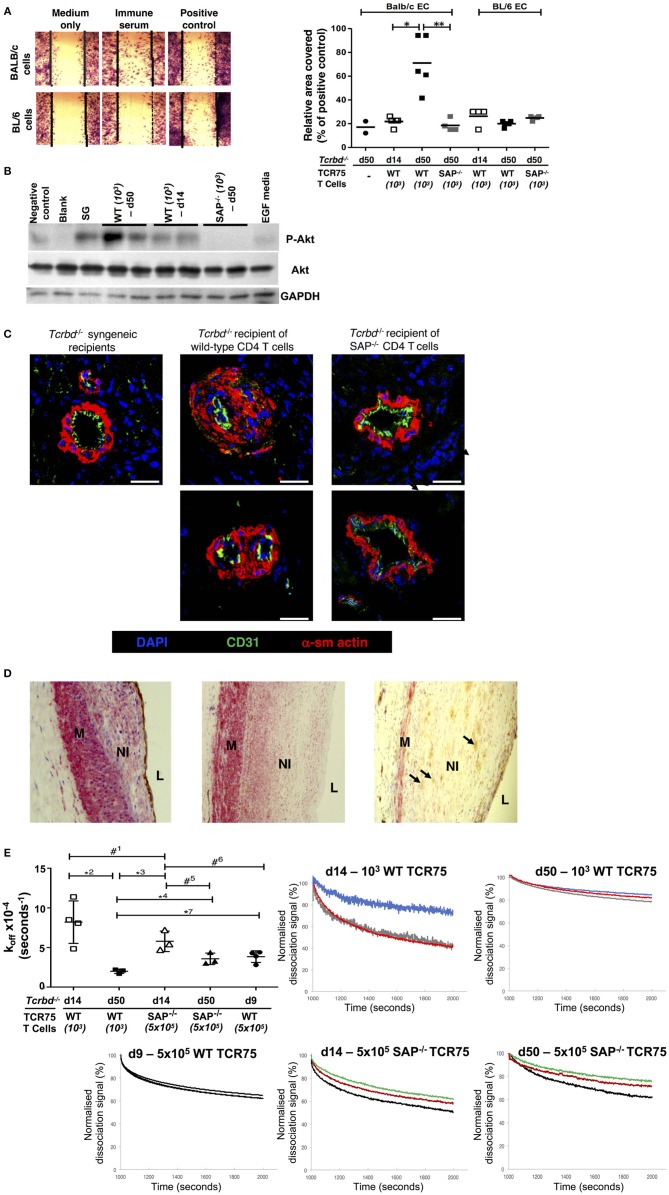
Alloantibody mediates endothelial activation and proliferative vasculopathy. (A) Representative photomicrograph of scratch-wound assay (left) and histogram (right) demonstrating enhanced migration of BALB/c endothelial cells (ECs) upon incubation with day 50 serum sampled from BL/6 Tcrbd−/− reconstituted with wild-type (WT) or SAP−/− TCR75 CD4 T cells, whereas BL/6 EC migration was not above background (mean values, with each dot representing an average of six high power fields analyzed per biological replicate). Migration of BALB/c ECs in response to sera from d14 WT or d50 SAP−/− was significantly weaker compared to serum from d50 WT recipients; *P = 0.01 and **P = 0.02, Mann–Whitney tests. (B) Quiescent BALB/c endothelial cells stimulated with media containing epidermal growth factor (EGF) or column-purified sera from: d50 non-reconstituted BL/6 Tcrbd−/− recipients of BALB/c grafts (negative control), d14 WT, d50 WT, d50 SAP−/− recipients, and pooled hyperimmune anti-H-2Kd IgG serum (BALB/c skin grafts [SG] to BL/6 mice, positive control). Cell lysates were separated and immunoblotted with anti-Akt Ser473, anti-phospho-Akt Ser473, and GAPDH (control) mAb. Displayed Western blot represents three independent experiments. (C) Representative photomicrographs of coronary arteries from allografts explanted at day 50 and double immunolabeled with endothelial marker CD31 (green) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-sm actin, red); scale bar−200 μm. Increased neointimal lesions in chronically rejecting BALB/c allografts containing a large number of α-actin–positive smooth muscle cells were observed in BL/6 Tcrbd−/− recipients reconstituted with 103 TCR75 T cells (middle column) but not with SAP−/− TCR75 CD4 T cells (right); Tcrbd−/− syngeneic grafts shown as comparison (left). (D) Representative photomicrographs of endomyocardial biopsies of human heart allografts in recipients with antibody-mediated rejection and double-immunostained with the endothelial marker CD31 (brown) and α-smooth muscle actin (red); magnification x25. Pronounced neointimal (NI) lesions, composed of dense smooth muscle cells (pink), lying between the media (M) and arterial lumen (L). Remnants of endothelial cell layer seen within neointima (arrows, right image). Images representative of staining patterns observed in three individual patients. (E) Ranking anti-H-2Kd alloantibody dissociation kinetics. Left: dot plot histogram comparing anti-H-2Kd alloantibody dissociation constants (koff) among BL/6 Tcrbd−/− recipients of BALB/c hearts reconstituted with either WT or SAP−/− TCR75 CD4 T cells (at d9, 14, and 50 as depicted). Each value (mean ± SEM) represents the koff after global fit of two serum dilutions of the same biological replicate (n = 3); #1P = 0.21, *2P = 0.01, *3P = 0.008, *4P = 0.02, #5P = 0.06, #6P = 0.05, #7P = 0.01; two-tailed Student's t-test. Right: graphs depict sensograms of anti-H-2Kd antibody dissociation rates in sera from BL/6 Tcrbd−/− recipients of BALB/c hearts reconstituted as shown, with each curve representing individual recipient mice.