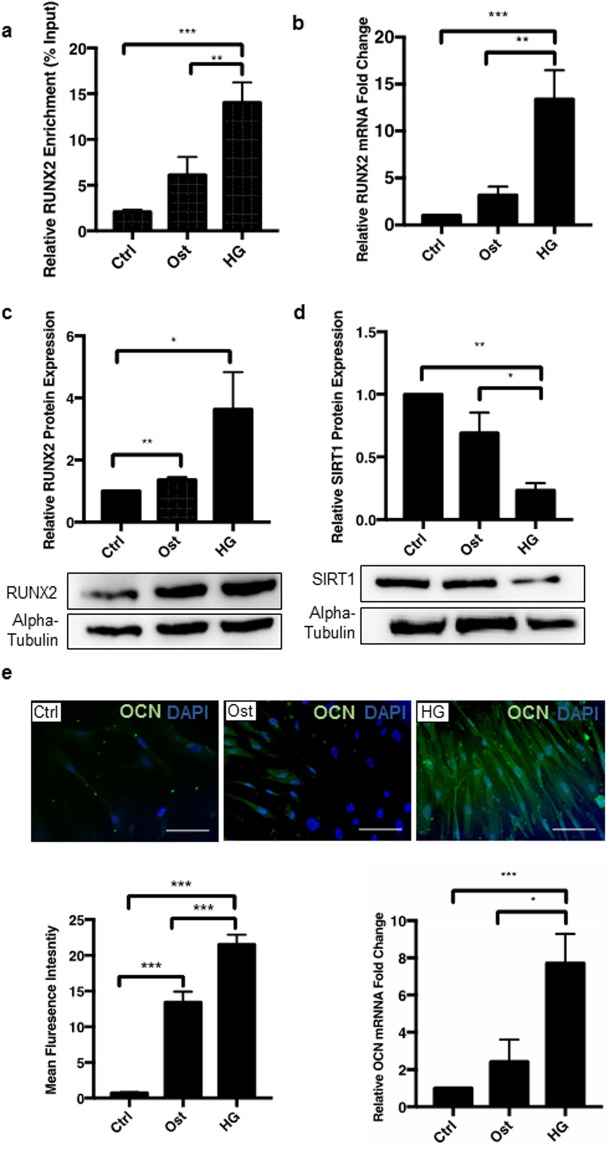
Figure 3.
Hyperglycaemic conditions increase RUNX2 promotor acetylation and protein expression of downstream markers. (a) Chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated a significant increase in acetylation of the RUNX2 promotor in hyperglycaemic conditions compared to both osteogenic and control (n = 3). (b) RUNX2 mRNA abundance was increased by over 10-fold in hyperglycaemic conditions compared to osteogenic and untreated controls (n = 9). (c) RUNX2 protein levels doubled in hyperglycaemic conditions compared to untreated controls, α-Tubulin shown as loading control (n = 3). (d) SIRT1 protein levels were significantly decreased by day 4 under hyperglycaemic conditions, compared to osteogenic conditions at day 4, with α-Tubulin as a loading control (n = 3). (e) OCN protein level assessed by fluorescent staining shown in green, increased by a third in hyperglycaemic conditions compared to osteogenic conditions (n = 4 and 5FoV). OCN mRNA abundance increased four-fold in hyperglycaemic conditions compared to osteogenic (n = 9). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001. Scale Bars = 10 μm.