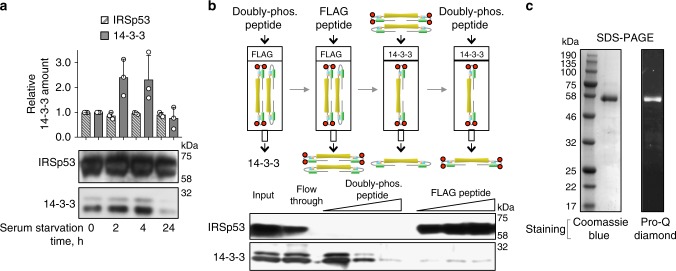
Fig. 1.
Purification of natively phosphorylated and 14-3-3-binding-competent pIRSp53. a Effect of serum starvation on the relative amount of 14-3-3 (gray bars) that coimmunoprecipitates with IRSp53-FLAG (stripped bars) from HEK293T cells. Error bars are ± s.d. from three independent experiments, shown as open circles. Abundance is reported relative to the amount of expressed IRSp53-FLAG or endogenous 14-3-3 in fed cells (first column). Note that serum starvation does not affect the expression of IRSp53-FLAG, but increases the relative amount of 14-3-3 that coimmunoprecipitates with it. An optimal starvation time of 2 h was established from these experiments. b Purification of phosphorylated IRSp53-FLAG from HEK293T cells. Cells were serum-starved for 2 h to enhance IRSp53 phosphorylation. Endogenous 14-3-3 bound to IRSp53 is competitively removed by addition of the doubly-phosphorylated IRSp53 peptide Sites 2,3 (Supplementary Table 1). The 14-3-3-binding-competent fraction of IRSp53 is then isolated through consecutive affinity purification steps (FLAG-affinity and 14-3-3-affinity), eluting IRSp53-FLAG by competition with either FLAG or Sites 2,3 peptides. c Coomassie and Pro-Q Diamond-stained SDS-PAGE gels showing that the isolated fraction of IRSp53 is pure and phosphorylated