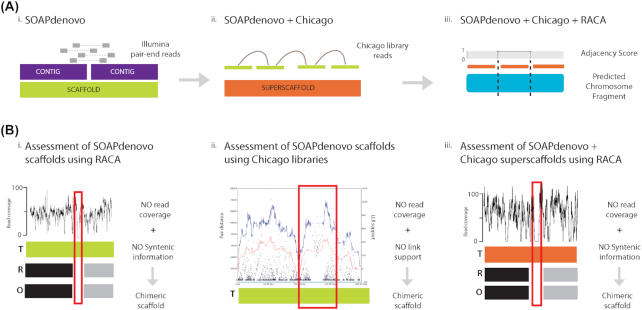
Figure 2:
Overview of the approach to generate a chromosome-level gemsbok genome assembly. (A) Illumina paired-end and mate-pair reads were assembled into contigs (purple) and then into scaffolds (green) using SOAPdenovo (i). These scaffolds were merged into superscaffolds (orange) using Dovetail Chicago methodology (ii) [11]. Finally, Reference-Assisted Chromosome Assembly tool (RACA) [13] was applied to produce chromosomal fragments (blue) from the superscaffolds (iii). (B) To reveal potential chimeric scaffolds, we used the information provided by RACA to identify regions with low read coverage and no syntenic information (demarcated with a red box) in scaffolds (i) or in superscaffolds (iii). The HiRise scaffolder used Chicago libraries sequencing data to pinpoint potentially chimeric regions (shown in the red box) with low read coverage and a substantial reduction of link support (ii). R: reference, T: target and O: outgroup genomes.