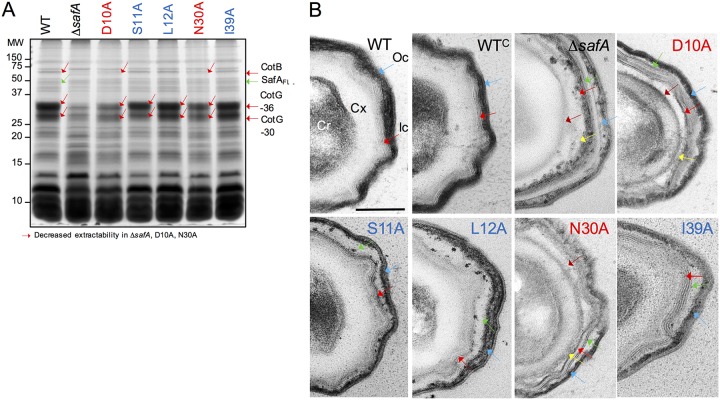
FIG 4.
Substitutions in the LysM domain affect the composition and structure of spores. (A) Spores were purified by density gradient centrifugation, and the coat proteins were extracted and resolved by SDS-PAGE. The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. Spores analyzed were from the WT, a ΔsafA in-frame deletion mutant, and derivatives of the ΔsafA mutant expressing alleles of safA coding for proteins with the indicated substitutions (color code as in Fig. 2) from the amyE locus. The proteins indicated with red arrows show decreased extractability from spores of the ΔsafA, D10A, and N30A mutant strains. The positions of molecular weight (MW) markers, in kilodaltons, are shown on the left side of the panel. (B) The same spores as in panel A were processed for analysis by transmission electron microscopy. Shown are representative specimens for the indicated strains. Cr, spore core; Cx, cortex; Ic, inner coat; Oc, outer coat. Red arrows, inner coat; blue arrows, outer coat; brown arrows, the space between the cortex and inner coat; green arrows, the space between the inner and outer coat; yellow arrows, partially unstructured material that accumulates at the inner edge of the inner coat. Scale bar = 0.2 µm.