FIGURE 6.
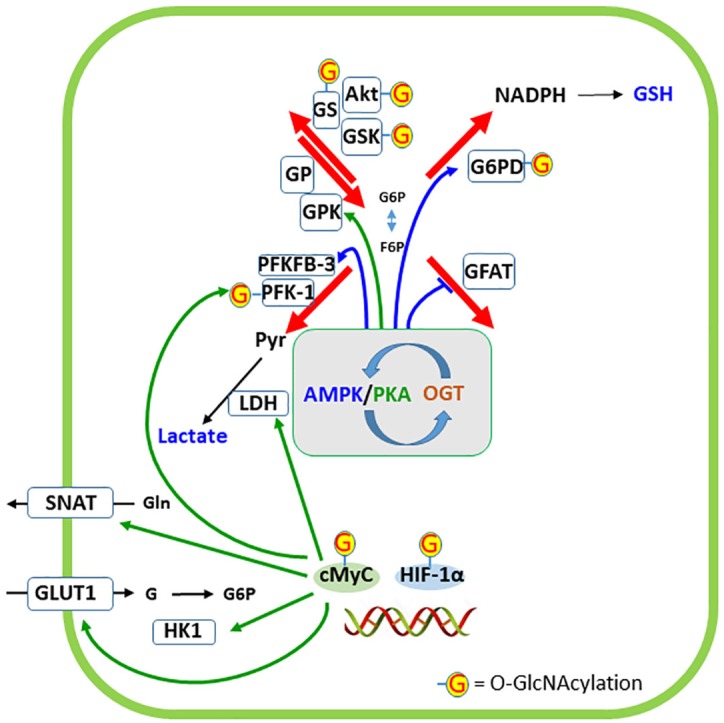
Regulation of cellular destinations of glucose by O-GlcNAc modification of proteins. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and protein kinase A (PKA) have a narrow interaction in the regulation of glucose metabolism as well as phosphorylate and are targets of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT). The phosphorylation of specific targets of AMPK or PKA in the four cellular destinations of glucose are indicated by the respective colored arrows. Targets of OGT are indicated by G. Two transcription factors closely related to glucose metabolism (cMyc and HIF-1α) are represented at the double-strand DNA and five proteins whose expressions are regulated by these transcription factors are indicated. G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFAT, glutamine:fructose-6P aminotransferase; GLUT1, glucose transporter 1; GP, glycogen phosphorylase; GPK, glycogen phosphorylase kinase; GS, glycogen synthase; GSK, glycogen synthase kinase; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HK1, hexokinase 1; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PFK-1, phosphofructokinase 1; PFKFB-3, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3; SNAT, sodium-neutral amino acid transporter (type 3 or 5, in astrocytes).
