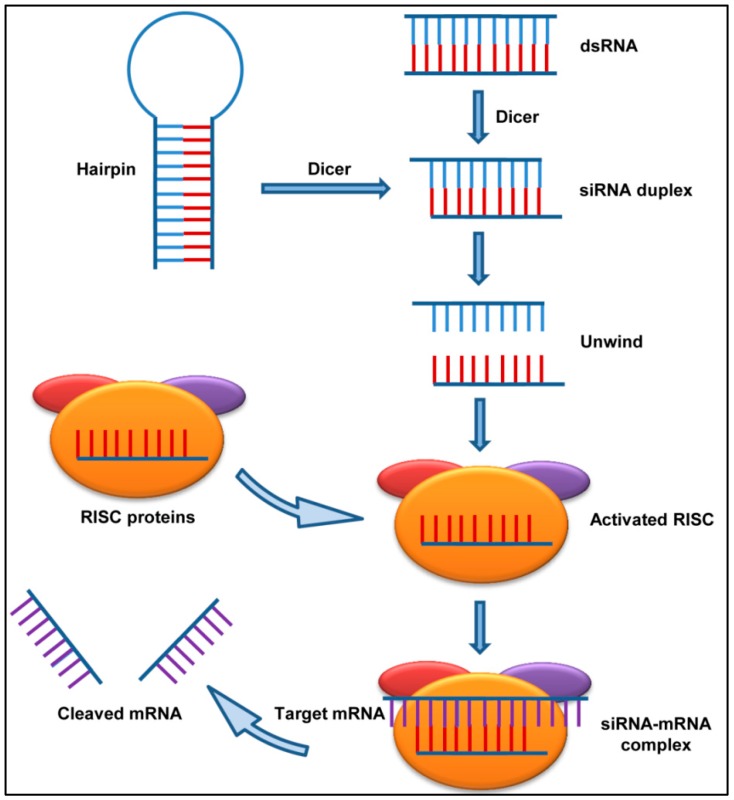
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of short interfering RNAs (siRNA): The presence of a double stranded RNA as a consequence of viral infection triggers RNA interference (RNAi). The host enzyme Dicer binds to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and cleaves it into short pieces of ∼20 nt called siRNA. One strand of the RNA associates with the RNA induced silencing complex (RISC) proteins and binds to the target mRNA. The mRNA is then cleaved by the nuclease activity of the RISC.