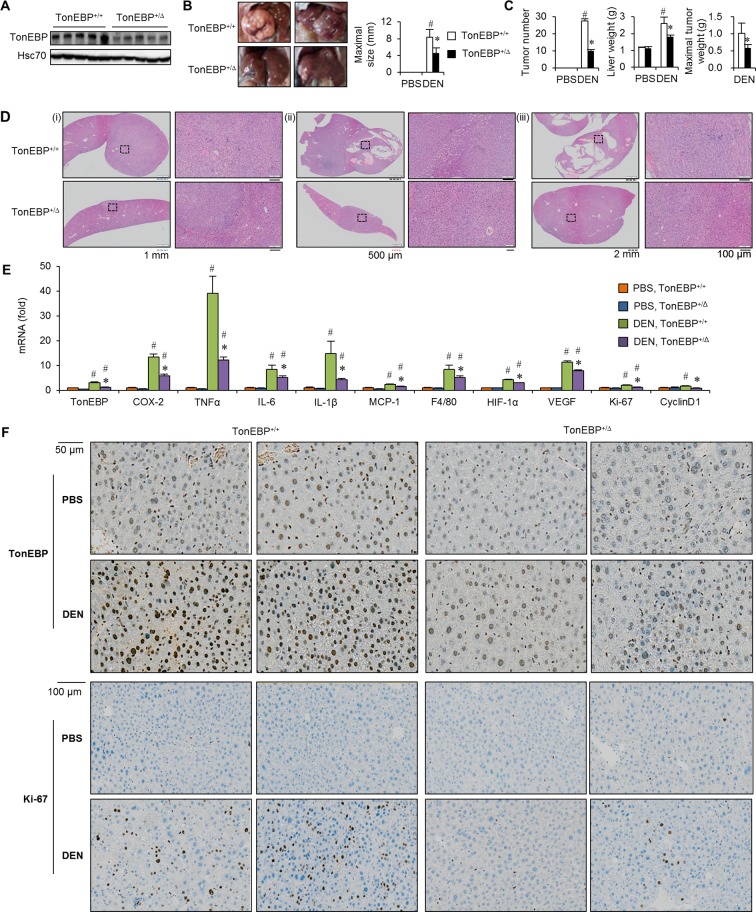
Figure 2.
TonEBP haplodeficiency is resistant to DEN-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. TonEBP+/Δ mice and their TonEBP+/+ littermates were treated with PBS or DEN as in figure 1. (A) Non-tumour regions adjacent to tumours were immunoblotted for TonEBP and Hsc70 from DEN-injected animals. (B) Representative liver images from DEN-injected animals. (C) Tumour number, maximal size of tumours and liver weight from PBS-injected (n=8 for each genotype) or DEN-injected mice (n=18 for each genotype). Mean+SEM. #P<0.05 compared with corresponding PBS-injected animals. *P<0.05 compared with DEN-injected TonEBP+/Δ animals. (D) Representative H&E images of hepatic tissues from DEN-injected animals. Magnified images on the right are from small boxes on the left. Boxes are in tumours (top and bottom of (i), top of (ii) and (iii)), dysplastic nodule (bottom of (ii)) or tumour-free area (bottom of (iii)). (E) real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analyses of TonEBP, inflammatory genes (COX-2, TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1), macrophage marker (F4/80), proliferation markers (Ki-67, cyclin D1) and angiogenic factors (HIF-1α, VEGF) in non-tumour regions adjacent to tumours in animals from (C). (F) Representative immunohistochemical images of TonEBP and Ki-67. COX-2, cyclo-oxygenase-2; DEN, diethylnitrosamine; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; IL, interleukin; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor alpha; TonEBP, tonicity-responsive enhancer-binding protein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.