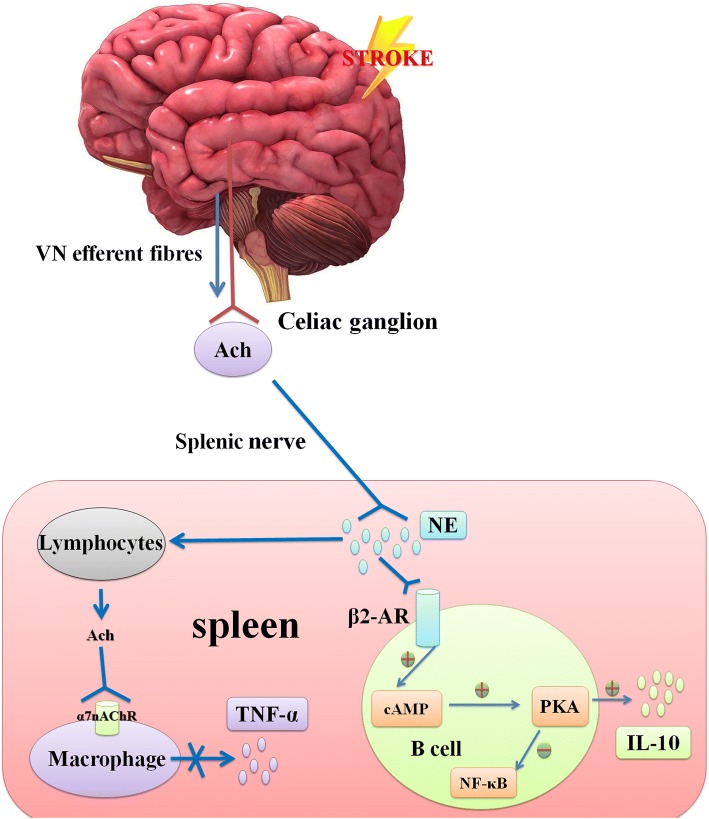
Fig. 5.
Splenic sympathetic nerve-mediated anti-inflammatory pathway after stroke. After the acute stage of stroke, “brain-spleen cross-talk” not only inhibits the splenic inflammatory response by activating the SNS (reducing the production of inflammatory factors, such as TNF-α) [172] but also induces IL-10 production by lymphocytes in the spleen through activation of the NE-mediated PKA/cAMP pathway in other inflammatory-related disease models [174, 175]