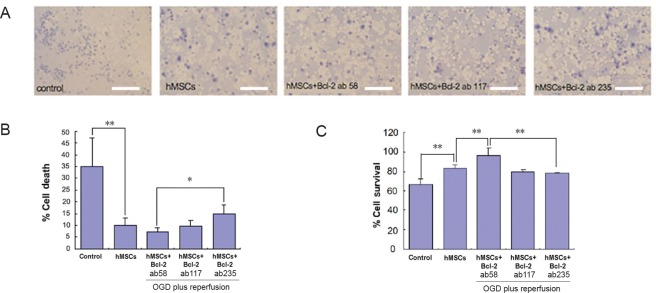
Figure 3.
Cell death (Trypan Blue assay) and cell survival (MTT assay) in OGD model for cerebral ischemia involving primary mixed cultures of rat neurons and astrocytes.
(A) Images of rat neuron and astrocyte cultures expressing dead cells (blue) in media with different treatment regimens. Scale bars = 50 µm. (B) There was a significant (P < 0.01) decrease in cell death between the control and hMSCs groups. In contrast, the hMSCs + Bcl-2 antibody (235 ng/mL) group showed a significant (P < 0.05) increase in cell death compared to the hMSCs + Bcl-2 antibody (58 ng/mL) group. The dose of Bcl-2 antibody was 58, 117, or 235 ng/mL. All experiments were conducted in triplicates. (C) A graphical representation showing the significance between different treatment regimens. Cell survival significantly (P < 0.01) increased when treated with hMSCs and hMSCs + Bcl-2 antibody (58 ng/mL). However, when increased amounts of Bcl-2 antibody was administered, a significant (P < 0.01) decrease can be seen in the 117 ng/mL and 235 ng/mL groups. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance followed by post hoc Fisher’s protected least significant difference. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. hMSCs: Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; OGD: oxygen glucose deprivation; MTT: 3-(4,5-dimethylthianol-2-yl)-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide.