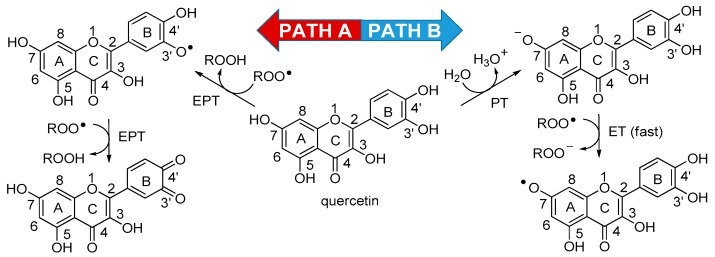
Scheme 1.
Possible reaction pathways for quercetin in water. Two mechanistic possibilities, arising from current literature, could account for the antioxidant activity of quercetin in water solution: Path A illustrates the electron–proton transfer (EPT) to peroxyl radicals from the catechol moiety, while Path B depicts the sequential proton loss electron transfer (SPLET = PT/ET) to water/peroxyl radicals. ET: Electron transfer; PT: Proton transfer.