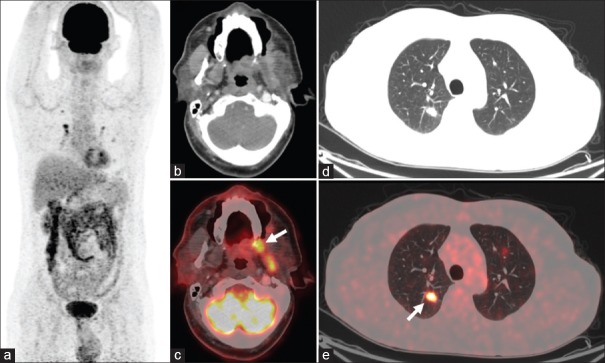
Figure 1.
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography maximum-intensity projection (a), transaxial computed tomography, and fused positron emission tomography/computed tomography images showing fluorodeoxyglucose-avid lesion in the region of left retromolar trigone (arrow; b and c) and buccal mucosa, eroding the adjoining alveolar plate and involving the left lateral pterygoid muscle. Multiple fluorodeoxyglucose-avid parenchymal nodules (arrow; d and e) noted in the bilateral lung fields