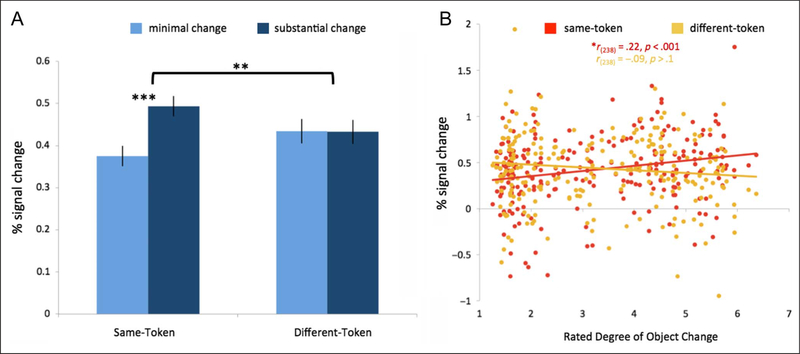
Figure 2.
Comparison of S-Token and D-Token conditions. (A) There is a significant effect of object change in the S-Token condition ( p < .001), but not in the D-Token condition ( p = .97). Error bars reflect the difference of the means. (B) Item analysis using object change as a continuous variable. Rated degree of object change predicts percent signal change for each item in the S-Token condition ( p < .001) but not in the D-Token condition ( p = .16).