Figure 2.
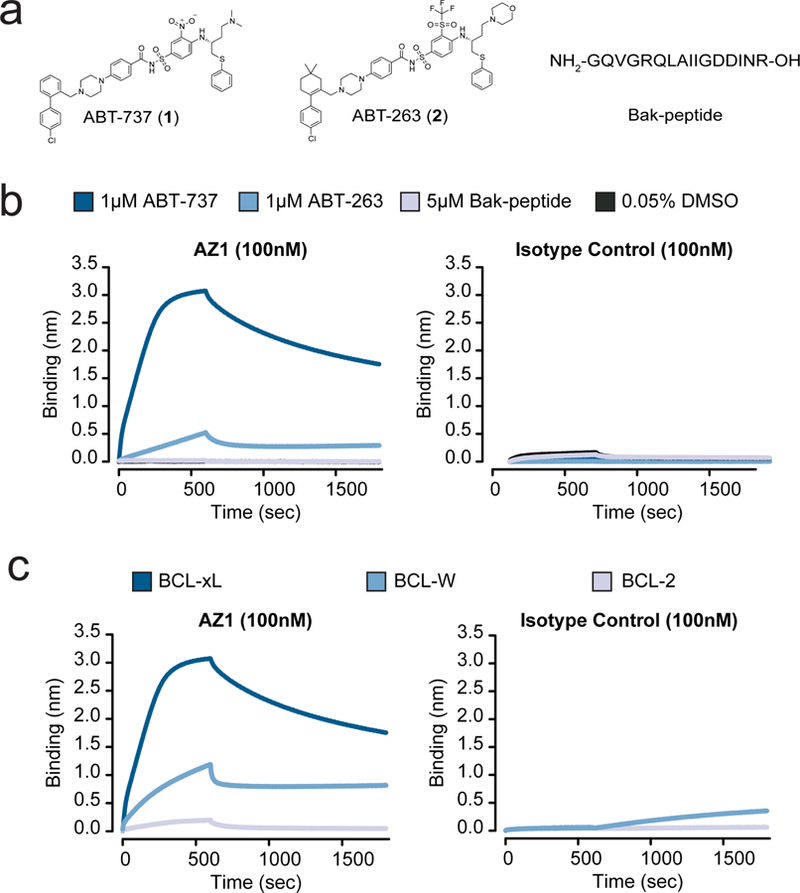
Characterization of the Fab AZ1 epitope. (a) Chemical structures and amino acid sequence of the binding ligands: ABT-737, ABT-263, and Bak-peptide. (b) Biolayer interferometry shows Fab AZ1 binds potently to BCL-xL in the presence of ABT-737, with greatly reduced potency in the presence of ABT-263, and weakly or undetectably in the presence of Bak-peptide. The data shows that AZ1 can readily discriminate between subtle structural differences in the small molecules, and supports that Fab AZ1 is chemical-epitope selective. The isotype control is a Fab selected against CD55, with an identical scaffold to AZ1 but differing CDR sequences. (c) Biolayer interferometry show Fab AZ1 binds potently to BCL-xL in the presence of ABT-737, with greatly reduced potency to BCL-W, and undetectably to BCL-2. The data shows that AZ1 can readily discriminate between subtle structural differences in the proteins, and supports that Fab AZ1 makes important contacts with BCL-xL in addition to its contacts with ABT-737. The isotype control is a Fab selected against CD55, with an identical scaffold to AZ1 but differing CDR sequences.
