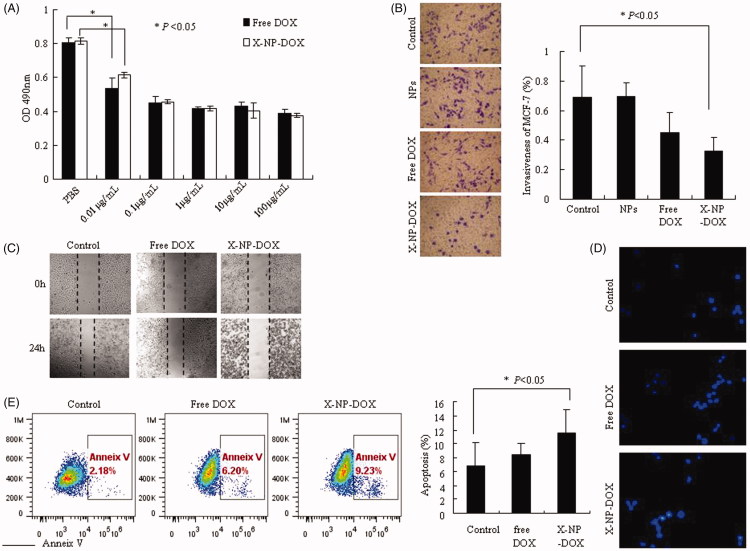
Figure 2.
Low-dose X-NP-DOX inhibits cell growth, migration, invasion, and induces cell apoptosis in vitro. The CCK8 assay, wound-healing assay, and Transwell chambers assay were used to analyze cell growth, migration, and cell invasion; cell apoptosis was measured by Hoechst 33258 staining or Annexin V staining. The CCK8 assay, wound-healing assay, transwell chambers assay, and apoptosis staining was performed as described in Materials and Methods section. (A) The antitumor activity of X-NP-DOX in MCF-7 by CCK8 assays. Under the treatment of X-NP-DOX or free DOX, the proliferation of MCF-7 cells was markedly inhibited compared with the PBS group (p < .05). (B) The transwell system assay illustrated that the invasiveness of MCF-7 was inhibited by low-dose X-NP-DOX (magnification, 400×). The transwell system assay showed that the percentage of MCF-7 invasiveness treated with X-NP-DOX was significantly lower than that of PBS-treated cells (p < .05). (C) The wound-healing assay showed that the number of migrating cells treated with low-dose X-NP-DOX was significantly less compared to free DOX and PBS groups. (D, E) Hoechst 33258 staining (D) and Annexin V-FITC staining (E) results showed that early apoptotic cells were observed in low-dose X-NP-DOX-treated group.