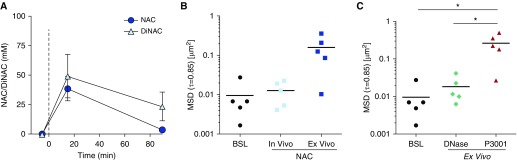
Figure 8.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) pharmacokinetics and mucolytic effects on cystic fibrosis (CF) sputum measured by microrheology. Five individuals with CF were treated with 20% (1.27 M) NAC via inhalation. Spontaneously expectorated sputa were collected 0, 15, and 90 minutes after treatment. (A) Sputum drug concentrations measured using mass spectrometry at 0, 15, and 90 minutes. (B) Sputum microrheology or mean square displacement (MSD) measured at baseline and 90 minutes after NAC treatment (in vivo) by tracking 1-μm fluorescence beads mixed in sputum specimens. In parallel, aliquots of sputa collected at baseline were incubated at 37°C with 100 mM NAC for 90 minutes (ex vivo). (C) MSD of baseline sputa incubated ex vivo at 37°C with 0.1 mg/ml rhDNase or 10 mM P3001 for 15 minutes. Passive bead diffusion (or MSD) is shown as scatter plot of MSDτ=0.83s for tracer particles in sputum for each treatment condition. *P < 0.05. BSL = baseline; DiNAC = N,N′-diacetyl-l-cystine.