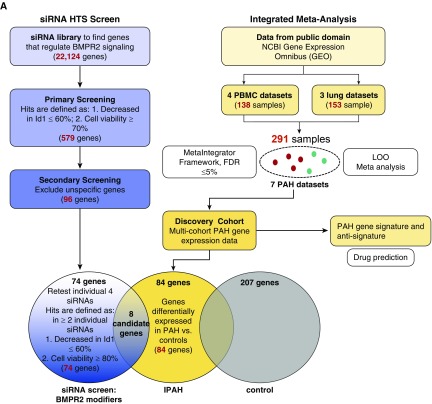
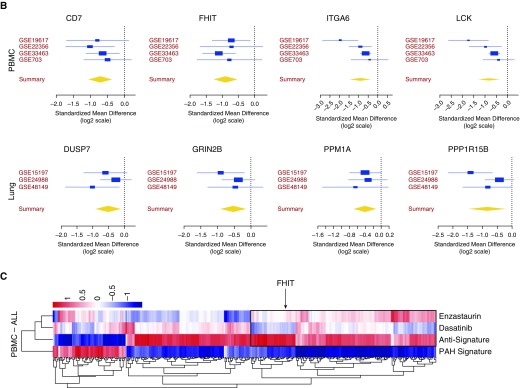
Figure 1.
Identification of BMPR2 regulatory genes by a siRNA high-throughput screen (HTS) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) meta-analysis. A mouse high-throughput siRNA screen of >22,000 genes was conducted, using an Id1-BRE luciferase reporter assay in a C2C12 mouse myoblastoma cell line treated with or without 250 pM BMP4, as previously described (12). BMP4 was conducted, as previously described (12). (A) Targets were identified by a decrease in Id1 expression ≤60% and viability ≥80% in response to stimulation, yielding 74 meaningful HTS candidates. To identify a PAH signature, the candidates were validated with gene expression data from an integrated meta-analysis algorithm of PAH lung and immune cell (peripheral blood mononuclear cell) datasets and a further validation cohort. (B) Of eight genes that were altered in patients with idiopathic PAH, fragile histidine triad expression was most consistently downregulated throughout all data sets. (C) PAH gene expression profile and antisignature compared with the gene signature of enzastaurin and dasatinib. BMPR2 = bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2; FDR = false discovery rate; FHIT = fragile histidine triad; IPAH = idiopathic PAH; LOO = leave-one-out; NCBI = National Center for Biotechnology Information; PBMC = peripheral blood mononuclear cells.