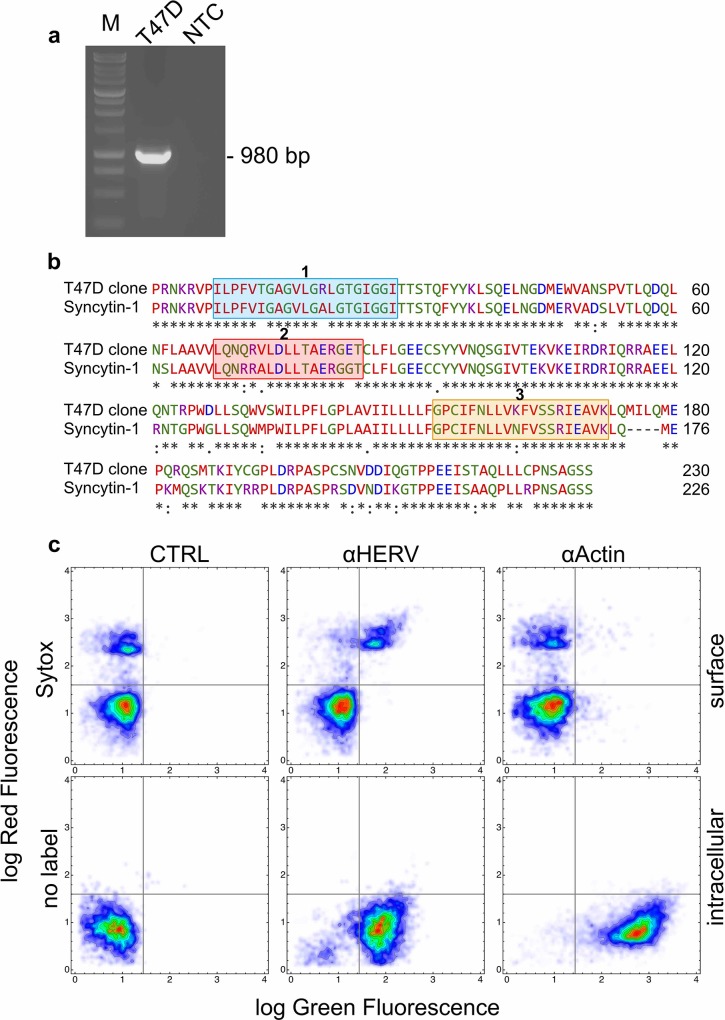
Fig 4. Expression of Syncytin-1 homologous DNA and protein sequences in T47D cells.
a: gel electrophoresis of the DNA fragment amplified by RT-PCR in extracts of T47D cells. The amplicon of 980 bp was obtained with a primer pair designed on the terminal 3' coding region and a portion of the 3' untranslated region of the Syncytin-1 (AF208161) transcript. M: molecular size marker; T47D: fragment amplified in T47D cells; NTC: no template control. The full-length gel is presented in Figure C in S1 File b: the deduced aminoacid sequence of the translated portion of the amplified fragment in a was aligned against the human Syncytin-1 protein sequence using the Clustal Omega software in search of homologies. The blue box 1 shows the known fusogenic peptide of Syncytin-1 [22] whereas the orange box 2 the domain of Syncytin-1 that is essential for its fusogenic activity [22]. The red box 2 shows the immunosuppressive peptide of Syncytin-1 [22]. T47 cells express a protein (SyHP) with elevated homology for Syncytin-1 c: two dimensional flow cytometry investigation of SyHP expression in T47D cells. We used an anti-HERV antibody (αHERV) raised against a central peptide of Syncytin-1. Anti-Actin (αActin) antibodies were used as control. Bound antibodies were revealed with secondary antibodies conjugated to FITC (green fluorescence). Non permeabilised cells were also labelled with the vital fluorescent dye Sytox (red fluorescence) that labels dying and dead cells. Nearly all cells showed intracellular expression of SyHP. SyHP translocated to the plasma membrane of Sytox+ cells.