Figure 1.
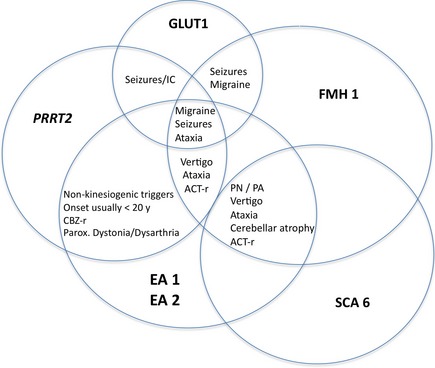
Clinical overlap of EA 1 and 2 and its differential diagnoses. ACT‐r, (possibly) acetazolamide responsive; CBZ‐r, (possibly) carbamazepine responsive; IC, infantile convulsions; PA, permanent ataxia; parox., paroxysmal; PN, permanent nystagmus; PRRT2, proline‐rich transmembrane protein gene (PRRT2) mutations.
