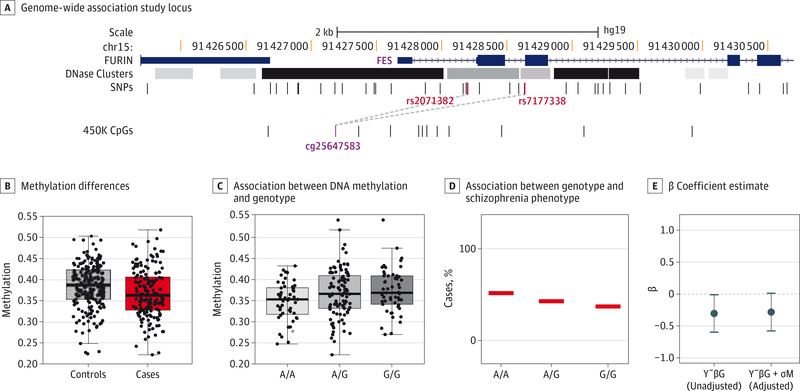
Figure 3. Genotype-Dependent Differentially Methylated Positions in Psychiatric Genomics Consortium Schizophrenia-Associated Locus.
A, Psychiatric Genomics Consortium Genome-Wide Association Study locus (region 11) with an overlapping schizophrenia (SZ)-associated CpG. Dashed lines indicate single-nucleotide polymorphism–CpG cisregulation between the 2 SZ–single-nucleotide polymorphisms and locus cg25647583. B, Methylation differences between SZ cases and controls at locus cg25647583. C, Association between DNA methylation and genotype. In the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium Genome-Wide Association Study , the A allele is the risk allele (odds ratio = 1.0662). D, Association between genotype and SZ phenotype. The risk allele has increased frequency in our SZ cases. E, β coefficient estimate of the dependence of genotype on SZ phenotype, before and after adjusting for methylation. Error bars represent the 95% CIs for the estimate of β.