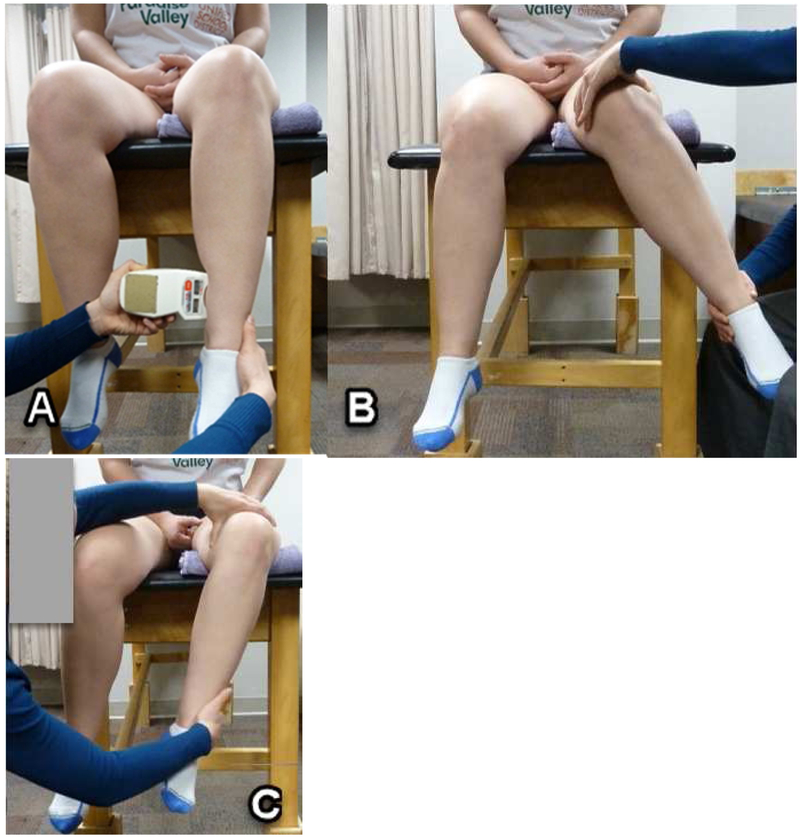
Figure 2.
Methods to assess hip rotation range of motion (ROM). (2A) Placement of the inclinometer. Position shown is for rotation ROM with the hip flexed to 90°. With the shank in vertical position, the inclinometer was placed four cm proximal to the medial malleoli and “zeroed” to eliminate the effect of tibial angulation on the final measure. For the Craig’s test and rotation ROM with the hip in neutral flexion/extension, the person was in prone, with the shank in vertical position. (2B) End of joint rotation range of motion (ROM) with the hip flexed to 90° for Hip internal rotation and (2C) for Hip exte rnal rotation. A folded towel was placed under the distal femur to ensure the 90° hip flexed position was attained. The pelvis and knee were monitored to prevent additional motion occurring at these adjacent joints.