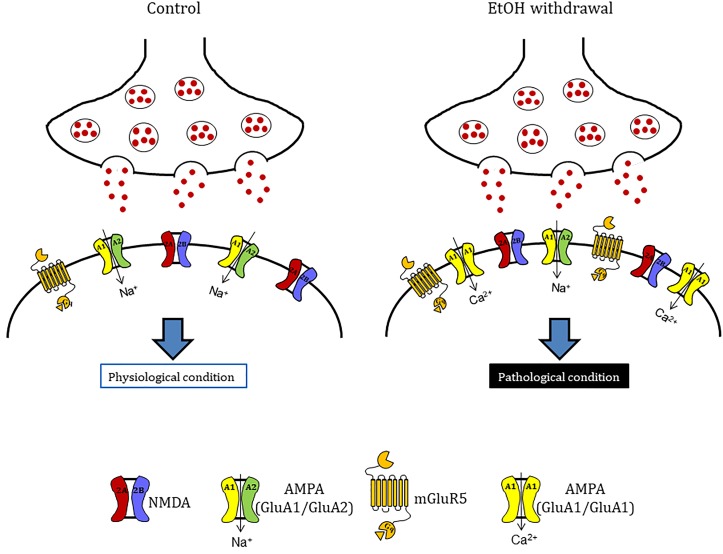
FIGURE 7.
Hypothetical model to explain mechanisms underlying ethanol withdrawal toxicity. Ethanol withdrawal potentiates the excitatory synaptic transmission that lead to CA1 injury of hippocampus in vitro. These alterations are probability due to the increase of the expression of the glutamate receptors AMPA (specifically the GluA1 AMPA subunit) and mGluR5. These evidences suggest that after ethanol withdrawal there is a shift in AMPAR subunit composition with the insertion of calcium permeable AMPA receptors in organotypic hippocampal slices.