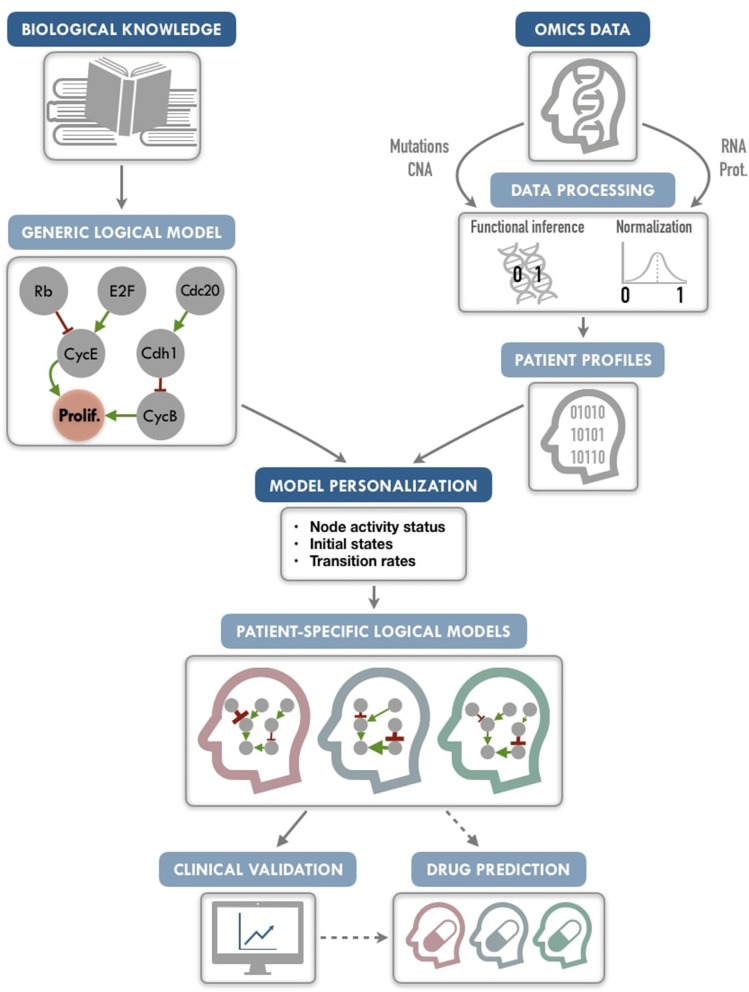
Figure 1.
PROFILE methodology for personalization of logical models. On the one hand (upper left), a generic logical model, in a MaBoSS format (a BND file for model description with logical rules and a CFG file for definition of the simulation parameters), is selected to serve as the starting-point. Note that any SBML qual model can be easily translated into a MaBoSS format. The parameters related to the nodes (initial states and transition rates) are chosen to be generic in the initial CFG file. On the other hand (upper right), omics data are gathered (e.g., genome and transcriptome) as data frames, and processed through functional inference methods (for already discrete genome data) or binarization/normalization (for continuous expression data). The resulting patient profiles are used to perform model personalization, i.e., adapt the generic model with patient data. The merging of the generic model with the patient profiles creates a personalized MaBoSS model with an unchanged BND file and a CFG file per patient. Then, clinical relevance of these patient-specific models can be assessed before providing original and personalized therapeutic strategies and drug predictions.