FIGURE 3.
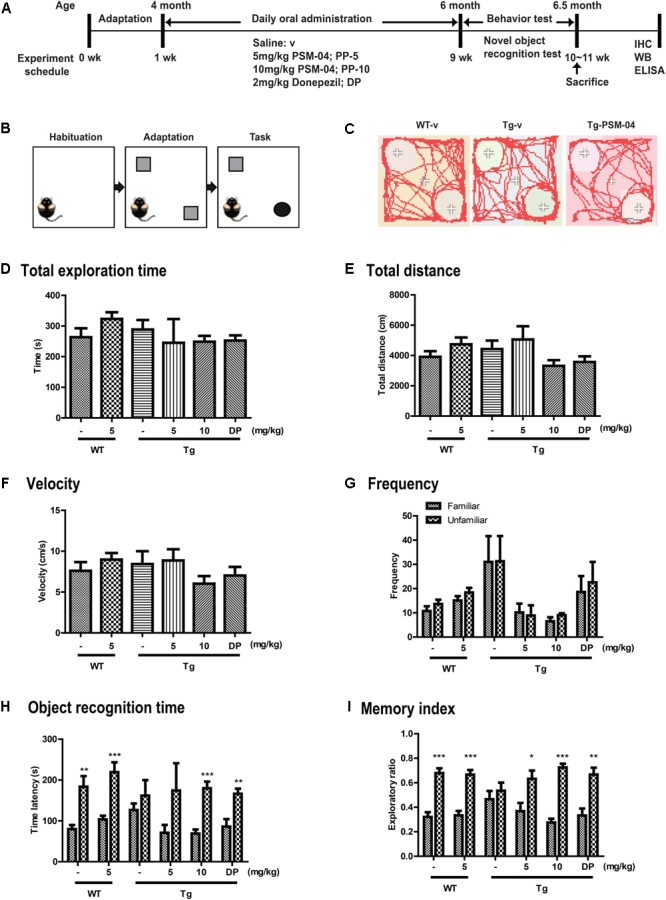
PSM-04 alleviated cognitive impairment in 5xFAD mice. (A) A schematic diagram of the in vivo experimental plan is shown. (B) The design of a novel object recognition (NOR) task is shown; in the habituation phase (30 min duration), mice were adapted to the open-field box. In the adaptation phase, the mice were exposed to two same objects. On the last day, one object was changed to a novel object and recorded for 10 min. (C) Representative track sheets showed alteration in locomotion and exploratory behavior in the NOR task (distance traveled to familiar vs. unfamiliar object). (D–I) Graphs represent total exploration time (D), total distances (E), velocity (F), frequency (G), objective recognition time (H), and the memory index (I). The statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA, and data are presented as means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Vehicle-treated WT mice (WT-v, n = 8); 5-mg/kg PSM-04-treated WT mice (WT-PP-5, n = 10); vehicle-treated Tg mice (Tg-v, n = 7); 5-mg/kg PSM-04-treated Tg mice (Tg-PP-5, n = 6); 10-mg/kg PSM-04-treated Tg mice (Tg-PP-10, n = 6); donepezil-treated Tg mice (Tg-DP, n = 5).
