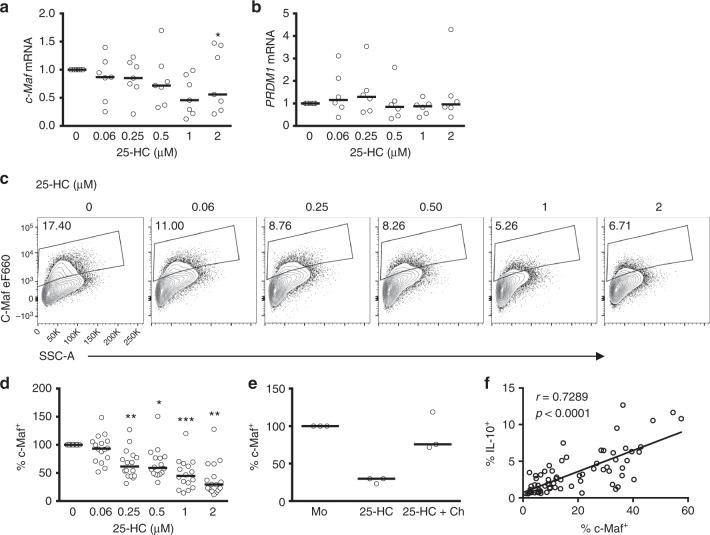
Fig. 5.
Cholesterol biosynthesis pathway inhibition interferes with c-Maf expression. Purified human CD4+ T cells stimulated in vitro with plate-bound α-CD3 (2 μgml−1) + α-CD46 (5 μgml−1) and recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) (50 Uml−1) were cultured for 36 h in the presence of 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-HC). a Expression levels of MAF mRNA (n = 7). b Expression levels of PRDM1 mRNA (n = 6). c Representative flow cytometric analysis of intracellular c-Maf staining. d Normalised frequency of c-Maf+ cells (n = 16). e Normalised frequency of c-Maf+ cells cultured under fully supplemented medium (M) and cholesterol (500×) (Ch) in the presence or absence of 2μM 25-HC (n = 3). f Correlation between frequency of c-Maf+ and IL-10+ cells, numbers denote r and p values for Spearman's correlation test. Graphs show independent donors (dots) normalised to untreated cells; bars represent median values. *<0.05 and **<0.01 denote a significant difference compared to untreated cells by Friedman test with post hoc Dunn’s correction (a) or by repeated-measures one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test with post hoc Dunnett’s correction (d)