Figure 7.
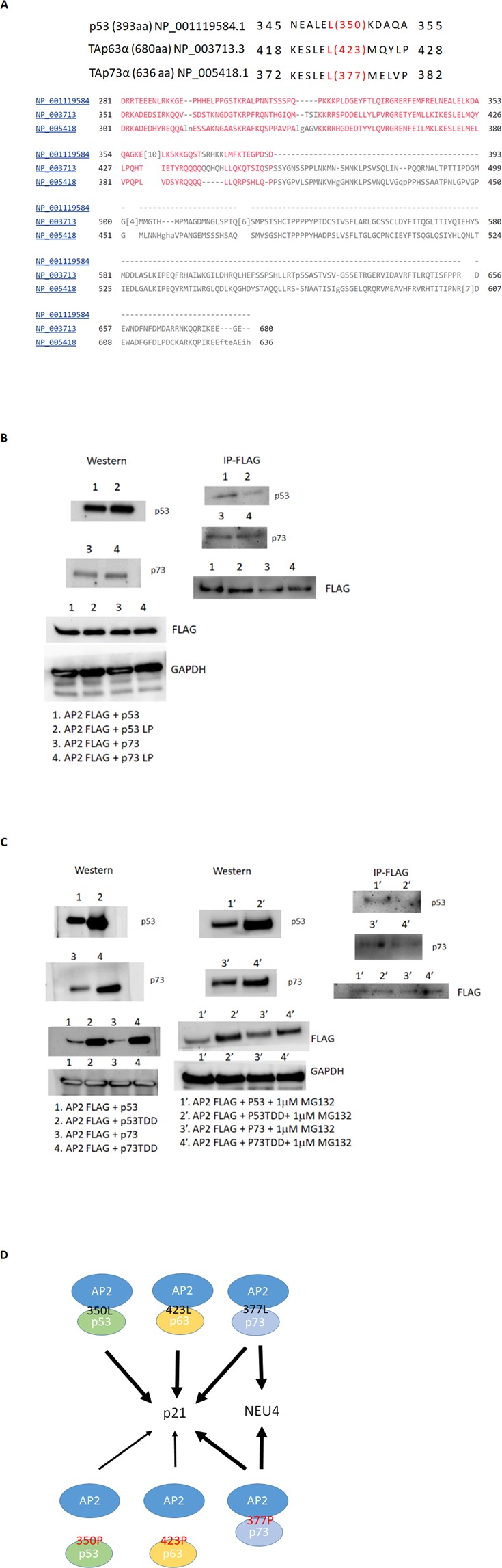
p73 exhibits a protein-protein interaction with AP2. (A) Partial sequence alignment within the tetramerization domains of p53 family members. COBALT61 was used for multiple protein sequences alignment of the C-terminal of p53 family members. (B) Flag-tagged AP2γ pulled down p53 and p73, albeit at lower amounts when p53LP was used (but not p73LP) in H1299 cells. (C) p53TDD and p73TDD (tetramerization domain deletion) influenced Flag-AP2γ expression, and this effect was reduced by adding MG132 (1 μM). Under treatment of MG132, p53TDD and p73TDD interaction with AP2γ were much less than that with wild-type p53 and p73. (D) A schematic figure explaining how the p53 WT or LP mutation regulates the p21 and NEU4 which contain both AP2 and p53 responsive elements. p53 family members can interact with AP2 to regulate down-stream genes. LP mutations of p53 and p63 lose the interaction with AP2 to regulate p21, but p73 LP mutant still interacts with AP2 to facilitate p21 and NEU4.
