Fig. 5. DNA methylation of NRE interferes with NREBP binding to increase HBV replication.
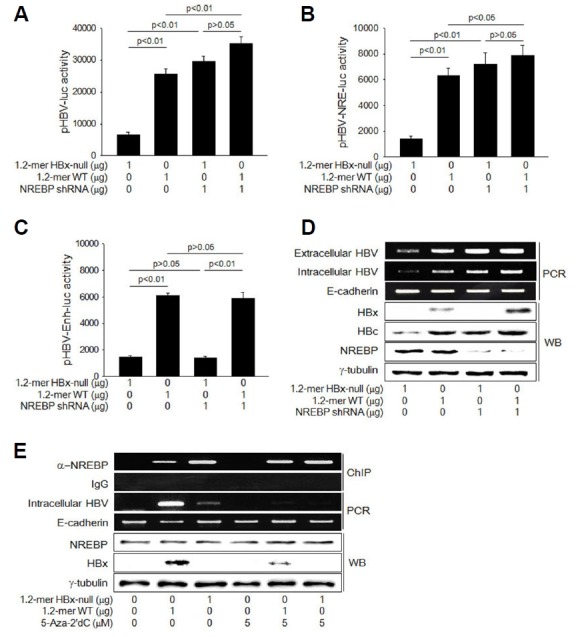
(A–C) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with pHBV-luc (A), pHBV-NRE-luc (B), or pHBV-Enh-luc (C) with either 1.2-mer WT or 1.2-mer HBx-null in the presence or absence of NREBP shRNA plasmid for 48 h, followed by luciferase assay (n = 5). (D) HepG2 cells were transfected with either 1.2-mer WT or 1.2-mer HBx-null with or without NREBP shRNA plasmid for 48 h. Levels of extracellular and intracellular HBV DNA and E-cadherin DNA as an internal control were determined by PCR (upper panels). Levels of HBx, HBc, and NREBP were determined by Western blotting (lower panels). (E) HepG2 cells were transfected with either 1.2-mer WT or 1.2-mer HBx-null for 48 h for 48 h in the presence or absence of 5 μM 5-Aza-2′dC. ChIP assay was performed to determine levels of NREBP bound on the NRE of HBV cccDNA (upper panels).
