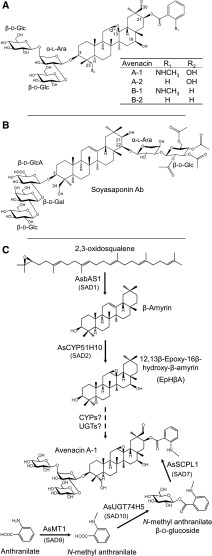
Figure 1.
Triterpene Glycoside Structures and Avenacin Biosynthesis.
(A) Avenacins: antifungal defense compounds from oat.
(B) Soyasaponin Ab, a triterpene glycoside associated with bitterness and anti-feedant activity in soybean.
(C) Current understanding of the avenacin biosynthetic pathway. The major avenacin, A-1, is synthesized from the linear isoprenoid precursor 2,3-oxidosqualene. 2,3-Oxidosqualene is cyclized by the triterpene synthase AsbAS1 (SAD1) to the pentacyclic triterpene scaffold β-amyrin (Haralampidis et al., 2001). β-Amyrin is then oxidized to EpHβA by the cytochrome P450 enzyme AsCYP51H10 (SAD2; Geisler et al., 2013). Subsequent, as-yet uncharacterized modifications involve a series of further oxygenations and addition of a branched trisaccharide moiety at the C-3 position, initiated by introduction of an l-Ara. Acylation at the C-21 position is performed by the AsSCPL1 (SAD7). The acyl donor used by AsSCPL1 is N-methyl anthranilate glucoside, which is generated by the methyl transferase AsMT1 and the glucosyl transferase AsUGT74H5 (SAD10; Mugford et al., 2009, 2013; Owatworakit et al., 2013).