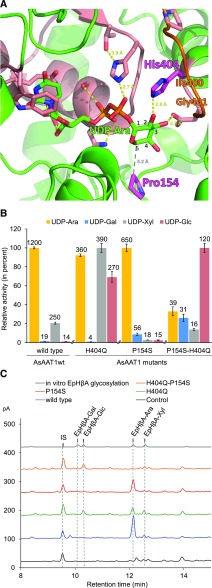
Figure 8.
Determinants of Sugar Donor Sugar Specificity of AsAAT1.
(A) Model of AsAAT1 with bound UDP-Ara (carbons of the Ara numbered). The protein is represented in green ribbons with the PSPG motif in salmon, including the side chains of highly conserved residues. The His404 and Pro154 residues are shown in magenta. Potential hydrogen bonds are shown with yellow dots, and the distance between P154 and C-5 of UDP-Ara with gray dots. The homology model was generated using I-TASSER software (Yang et al., 2015), based on the crystal structure of M. truncatula UGT71G1 complexed with UDP-Glc (PDB: 2ACW). The loop shown in orange was reconstructed using MODELER (Sali and Blundell, 1993). UDP-Ara was inserted into the active site and the complex was relaxed by energy minimization using GROMACS.
(B) Comparison of the glycosylation activity of the AsAAT1 wild-type and mutant enzymes when supplied with each of the four sugar donors (UDP-Ara, UDP-Gal, UDP-Xyl, or UDP-Glc). Initial velocities were measured using 30 µM deglycosylated avenacin A-1 as acceptor and 5 µM UDP-sugar donor using five time points. The heights of the bars are drawn relative to the highest activity observed for each recombinant enzyme (mean ± sd, n = 3). Activities reported above each bar are in nM.min−1.
(C) HPLC-CAD analysis of extracts from N. benthamiana leaves expressing SAD1 and SAD2 together with GFP (black), wild-type AsAAT1 enzyme (blue), AsAAT1-H404Q (green), AsAAT1-P154S (red), and AsAAT1-H404Q-P154S (orange). The top trace (in gray) shows the products of in vitro reaction of EpHβA with the four sugar donors (reactions performed separately and then pooled) for reference. LC-MS analysis was used to confirm the identities of the new products (Supplemental Figure 8C). The IS is digitoxin (1 mg/g dry weight).