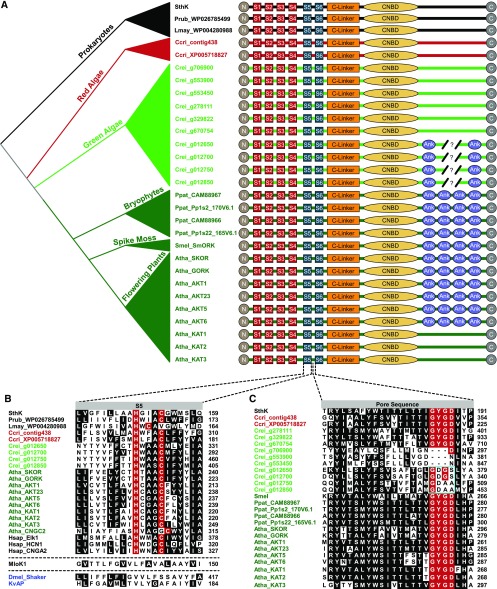
Figure 5.
Subunit Structure, S5 Transmembrane Domain and Pore Sequence for Plant VG K+ Channels and Select Algal and Prokaryotic CNBD Channels.
(A) Subunit structures compared among prokaryotic CNBD superfamily channels (black, SthK, Spirochaeta thermophila, Lmay, Leptospira mayottensis, Prub, Planktothrix rubescens); predicted CNBD channel sequences from red algae (red,Ccri, Chondrus crispus) and green algae (light green, Crei, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii); and land plants (dark green, Atha, Arabidopsis thaliana, Ppat, Physcomitrella patens, Smel, Selaginella moellendorffii). Amino acid sequences for the channels can be found in the Supplemental Data Set. Evolutionary relationships between the organisms are indicated in the schematic phylogeny at the left margin. Four VSD transmembrane domains (S1-S4) are depicted with red boxes, two pore helices (S5, S6) with blue boxes, the C-linker with an orange rectangle, the CNBD with a yellow ellipse and ankyrin repeats (Ank) with purple elipses. VG K+ channels in land plants contain 4 or 0 ankyrin repeats, while numbers vary in the four ankyrin repeat-containing gene predictions from green algae (broken line, 4 to 6 repeats) and final numbers have not been confirmed by cloning.
(B) Alignment of the S5 transmembrane domain of the PD from select CNBD family channels from eubacteria, algae, land plants, and metazoans (Hsap_Elk1, NP_653234; Hsap_HCN1, NP_066550; Hsap_CNGA2, NP_005131) illustrates the HXXXC motif characteristic of CNBD channels with MLoK1 (Mesorhizobium loti, WP_010911524), Shaker (Dmel, Drosophila melanogaster, NP_523393), and KvAP provided for comparison. Dotted lines separate MLoK1 and Dmel_Shaker/KvAP to signify they belong to different gene superfamilies. Identical or conservatively substituted residues present in >50% of the sequences are shaded, and the histidine and cysteine of the HXXXC motif are highlighted in red. Note that the cysteine is offset in Arabidopsis CNGC2 and a prokaryotic sequence from Leptospira mayottensis. Sequence positions are listed at the right margin; sequence names (left margin) contain species prefixes and are colored by phylogenetic group as in Figures 4S and 5A.
(C) Amino acid alignment of the pore loop between S5 and S6 with the canonical K+ channel selectivity filter residues (G-Y/F-G-D/N) highlighted in red. Residues conserved or conservatively substituted in >50% of the sequences at other positions are shaded black. Note the lack of conservation in the filter sequence in the four ankyrin repeat-containing green algae orthologs of the plant VG K+ channels (cyan box), suggesting they might not be K+-selective. Sequence names (left) are colored by phylogenetic group as in (A) and (B), and amino acid positions are given at the right margin. Sequences used in the alignments of (B) and (C) can be found in the Supplemental Data Set or have the accession number listed in the figure or legend.