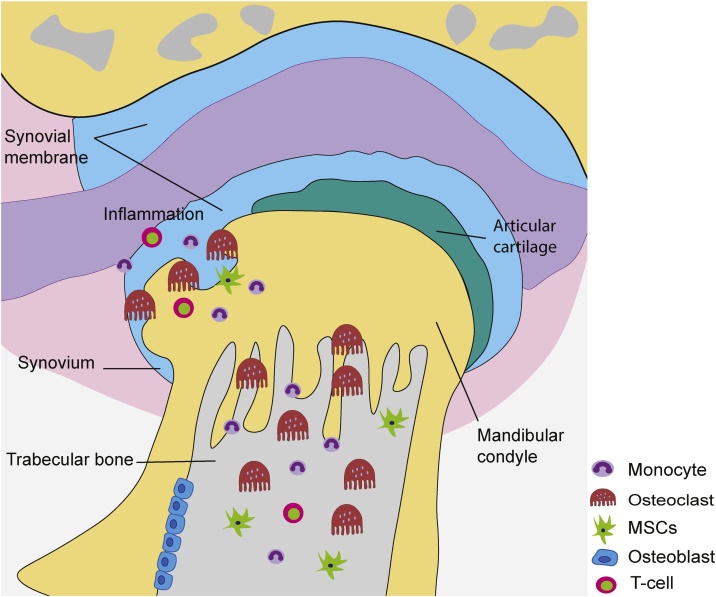
Fig. 1.
Bone destruction associated with TMJ-RA. RANKL is produced by T cells and inflamed synovium (synovitis) tissue. The presence of this cytokine in the TMJ leads to the local destruction of cartilage and eventually severe subchondral trabecular bone loss as a result of the recruitment and enhanced differentiation of osteoclast progenitor cells (monocytes) concomitant with a decrease in the recruitment and differentiation of osteoblast progenitor cells and MSCs.