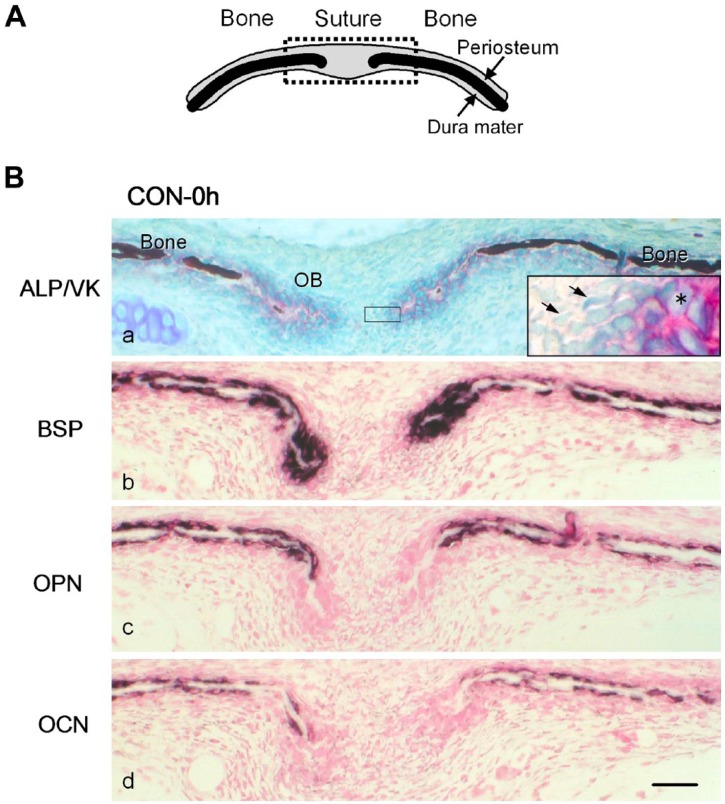
Figure 2.
(A) A schematic frontal view of the sagittal suture and parietal bones. The upper and lower sides of the suture and bones are the periosteum and dura mater, respectively. The dotted square indicates the area shown in (B). (B) Distribution of mRNA expression for non-collagenous bone matrices in the frontal sections of the sagittal suture and parietal bones from 4-day-old mice inspected immediately after excision (CON-0 h). (a) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity (red) was detected on the cell surface of cuboidal osteoblasts (OB) on the bone matrix. The mineralized matrix (dark brown) was detected by von Kossa staining (VK). Unmineralized osteoid was observed at the ends of parietal bones. The inset is a higher magnification of the squared area. Asterisk: ALP-positive osteoblasts. Arrows: fibroblast-like cells. (b, c, d) Specific transcripts for bone sialoprotein (BSP) (b), osteopontin (OPN) (c), and osteocalcin (OCN) (d), detected with antisense probes for in situ hybridization, are shown in dark purple. Scale bar: 50 μm. Abbreviation: CON, control group.