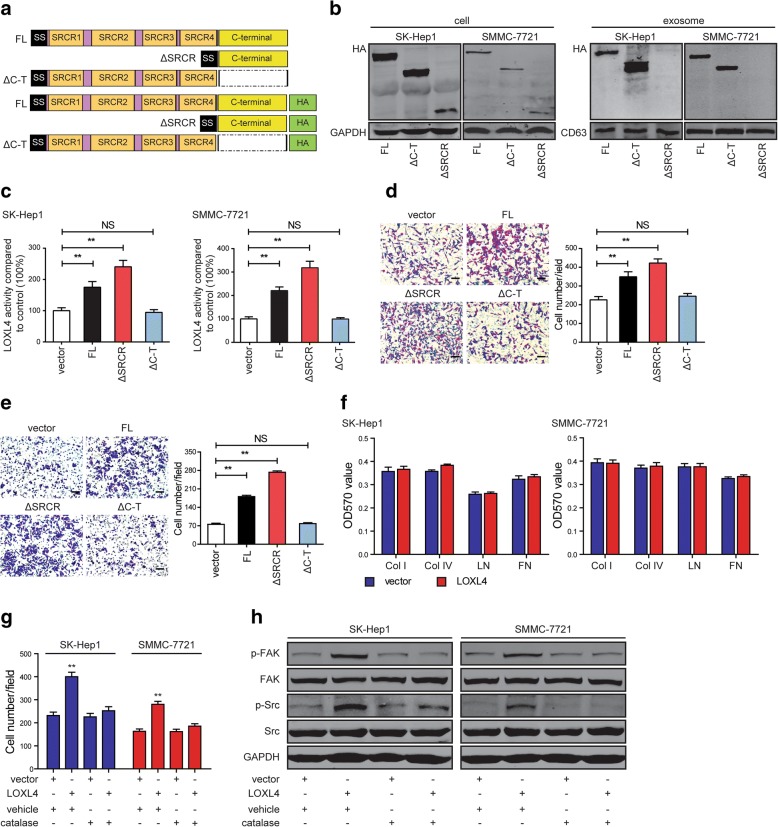
Fig. 5.
LOX catalytic activity is responsible for LOXL4 to promote cell-matrix adhesion and cell migration. a Domain structure of wild-type LOXL4 protein (full-length, FL) and deletion mutants thereof lacking the SRCR domains (ΔSRCR) and the C-terminal catalytic region (ΔC-T) with or without the HA-tag. b Analysis of the LOXL4-HA chimeras stably expressed in HCC cells and their corresponding exosomes by western blotting using an anti-HA antibody. c Intracellular LOXL4 catalytic activity measured in whole-cell lysates of control, FL, and deletion mutant cells. d-e Cell migration potential was determined in SK-Hep1 (d) and SMMC-7721 (e) cells transfected with FL, deletion mutants or control vector according to Transwell assays (Scale bar: 100 μm). f LOXL4-overexpressing and control cells were subjected to cell-matrix adhesion assay to Col I, Col IV, LN, and FN with catalase treatment (500 U/ml) for 12 h. g Cell migration potential was determined in LOXL4-overexpressing and control cells upon treatment with vehicle or catalase according to Transwell assays. h Western blotting analysis of phosphorylation of FAK and Src and total FAK and Src in LOXL4-overexpressing and control cells with vehicle or catalase treatment. (** P < 0.01)