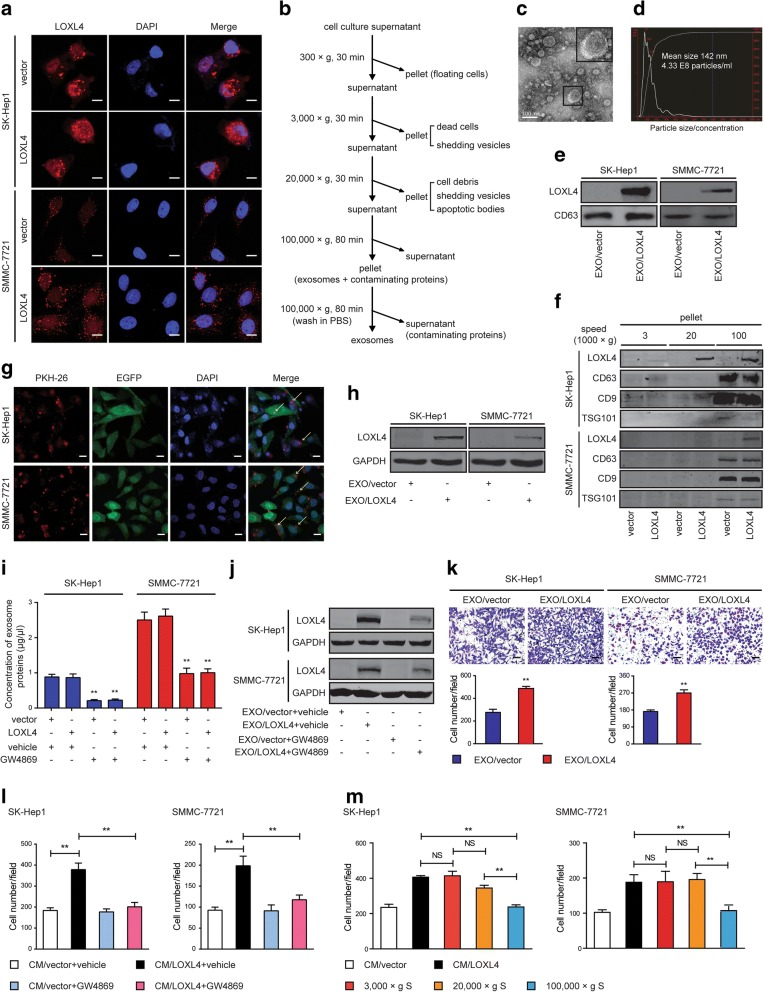
Fig. 7.
Intercellular transfer of LOXL4 by exosomes though autocrine/paracrine mechanisms to promote HCC migration. a IF images of LOXL4 in LOXL4-overexpressing and control cells. Red: LOXL4; Blue: DAPI (nuclei) (Scale bar: 100 μm). b Flow chart for the exosome purification procedure based on differential ultracentrifugation. c. electron microscopy of purified exosomes derived from SK-Hep1 cells overexpressing LOXL4 (Scale bar: 100 nm). d Characterization of purified exosomes derived from SK-Hep1 cells overexpressing LOXL4. Assessment of size, number, and distribution by NTA technology. e Western blotting analysis of exosomal marker CD63 and LOXL4 in exosomes purified from LOXL4-overexpressing cells (EXO/LOXL4) and control cells (EXO/vector). f Western blotting analysis of the corresponding pellets produced by differential ultracentrifugation for CD63, CD9, TSG101 (exosome marker proteins) and LOXL4. g Parental HCC cells expressing EGFP were incubated with PKH26-labelled EXO/LOXL4 for 2 h, and the arrows indicate exosomes incorporated into HCC cells. (Scale bar: 100 μm). h Detection of LOXL4 in parental HCC cells incubated with EXO/LOXL4 and EXO/vector by western blotting. i The effect of GW4869 (5 μM, 72 h) on the concentration of exosomes measured by BCA protein assay. j Detection of LOXL4 in parental HCC cells treated with exosomes derived from LOXL4-overexpressing and control cells incubated with vehicle or GW4869. k Cell migration potential was determined in SK-Hep1 and SMMC-7721 cells upon treatment with EXO/vector or EXO/LOXL4 (50 μg/ml) (Scale bar: 100 μm). l Cell migration potential was determined in SK-Hep1 and SMMC-7721 cells upon treatment with the CM from LOXL4-overexpressing and control cells incubated with vehicle or GW4869. m Cell migration potential was determined in SK-Hep1 and SMMC-7721 cells upon treatment with supernatant acquired by differential ultracentrifugation (supernatant, S). (** P < 0.01)