Fig. 3.
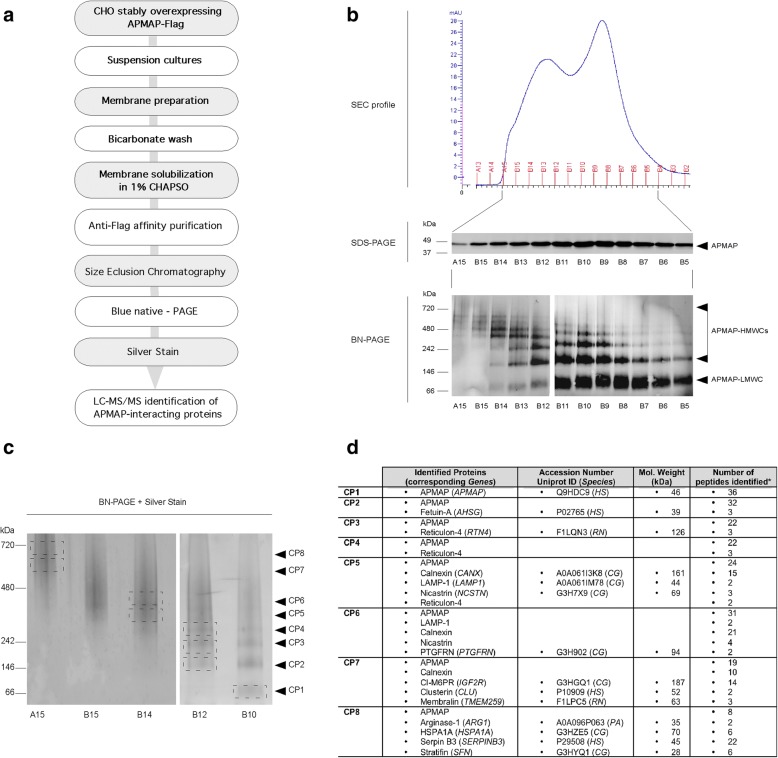
Purification of APMAP protein complexes and identification of APMAP interacting proteins. a Schematic representation of the multistep process designed for the purification of APMAP protein complexes and for the identification of APMAP interactomers. b Affinity purified APMAP protein complexes of different sizes were separated by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) on a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column. The SEC protein elution profile (top) revealed a protein distribution over 12 SEC fractions (A15 to B5), separated under denaturing conditions (SDS-PAGE) and immunostained with an anti-APMAP antibody (middle) or separated by blue native-PAGE (BN-PAGE) on a 4-16% Bis-Tris gel, and immunostained for APMAP (bottom). APMAP protein complexes appeared on the native gel as a low-molecular-weight complex (LMWC) of ~60 kDa and high-molecular-weight complexes (HMWCs) of ~150 to ~650 kDa. c Mass spectrometric identification of APMAP interacting proteins. The APMAP-containing low- and high-molecular-weight complexes from selected SEC fractions A15, B15, B14, B12 and B10 were resolved by native-PAGE on a 4-16% Bis-Tris gel, stained by silver nitrate, and the bands corresponding to eight different protein complexes (CP1 to CP8) were excised for protein content analysis by LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry. d Summary table of APMAP-interacting proteins identified by LC-MS/MS in CP1 to CP8. *Proteins and peptides identified by LC-MS/MS are listed in Additional file 1 Figure S4