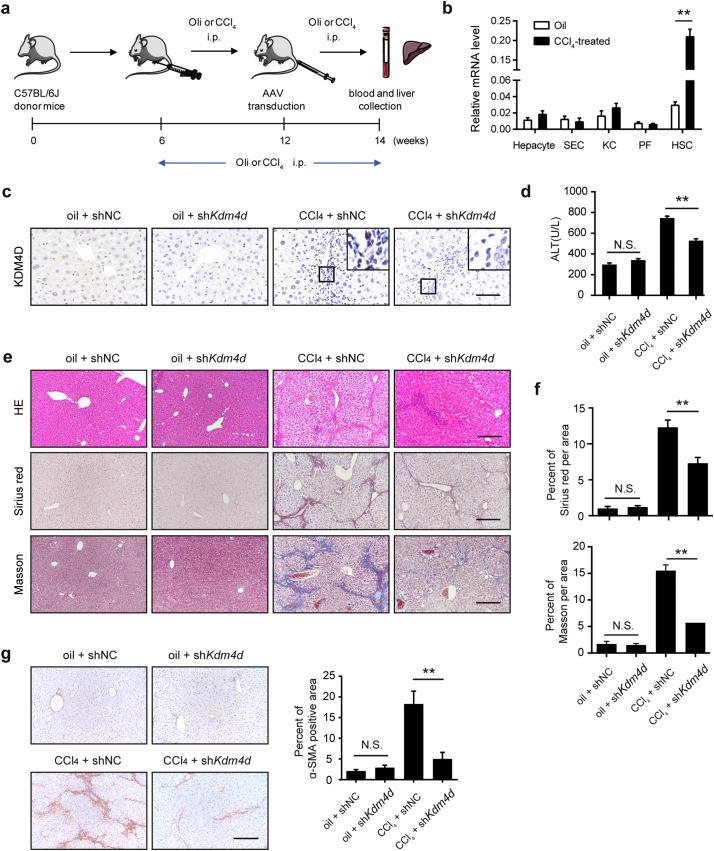
Fig. 3.
Kdm4d deficiency ameliorates liver fibrosis in mice. (a) The experiment scheme for Kdm4d knockdown in vivo. Liver fibrogenesis was induced by CCl4 injury using intraperitoneal injection twice a week from 6 to 14 weeks of age. Their counterparts were injected with oil. At week 12, shRNA expression vectors GFP carrying shRNA targeting Kdm4d or negative control were transfected into mouse liver through tail vein injection. Animals were humanely sacrificed, and their blood and liver samples were collected at week 14. (b) RT-qPCR analysis of Kdm4d mRNA level in HSCs, hepatocytes, sinusoidal endothelial cells (SEC), Kupffer cells (KC), and portal myofibroblasts (PF) isolated from the normal or CCl4-indced mouse liver tissues. (c) Representative IHC images of KDM4D in indicated groups. Scale bar, 200 μm. (d) The liver injury in each group was measured by ALT levels. (e) Representative histology images of H&E, Sirius red and Masson's trichrome staining in indicated groups. Scale bar, 200 μm. (f) Sirius red and Masson's trichrome positive areas were measured by Image J software. (g) Representative IHC images of α-SMA in indicated groups. Positive α-SMA staining area was measured by Image J software. Scale bar, 200 μm. Abbreviation: NS: not significant, shNC, empty vehicle alone. Data were presented as mean ± SD, **p < .01.