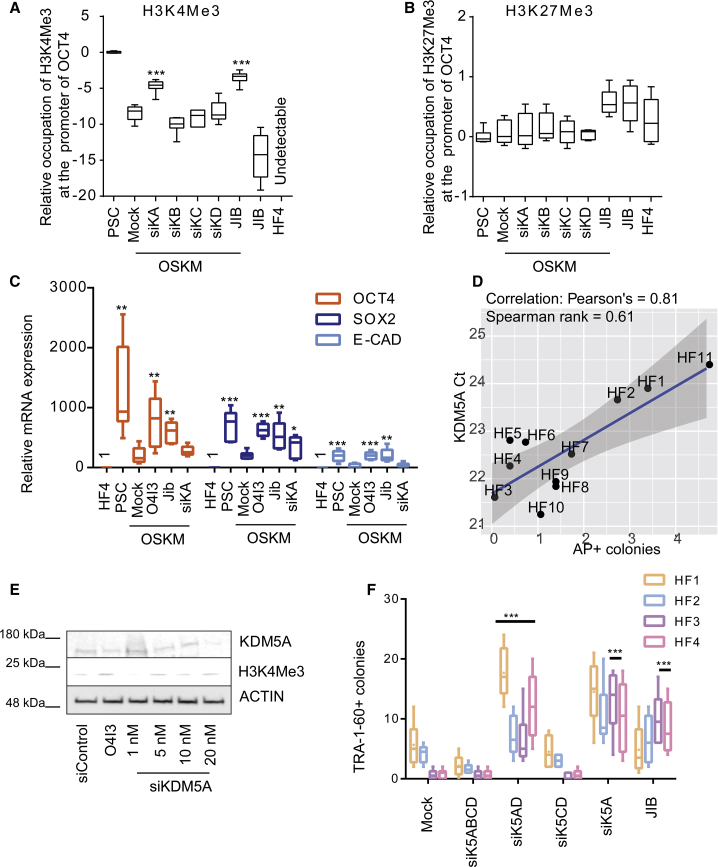
Figure 5.
KDM5A Is a Reprogramming Barrier
(A and B) (A) Suppression of KDM5A activity by siRNA or JIB-04 (5 μM, 48 h) promotes the enrichment of H3K4Me3 at the promoter of OCT4 in resistant fibroblasts, (B) but not that of H3K27Me3. Ct values were obtained from qRT-PCR.
(C) Suppression of KDM5A activity by JIB-04 or KDM5A siRNA (siKA) induces POU5F1, SOX2, and CDH1 mRNA levels during reprogramming, as determined by qRT-PCR.
(D) Correlation between reprogramming efficiency and KDM5A expression in HF1-HF11. The same amount of each cDNA was used as template for qRT-PCR where the Ct values indicate the expression of KDM5A.
(E) Knockdown effects of increasing concentrations of anti-KDM5A siRNA (siKDM5A, 48 h) on H3K4Me3 expression levels in HF.
(F) Reprogramming efficiency using various patient primary fibroblasts, as determined by the number of TRA-1-60-positive colonies. Cells were either transiently transfected with the indicated siRNA oligos in the first 5 days or treated with JIB-04 (5 μM, 48 h). siK5ABCD, anti-KDM5A/B/C/D siRNA; siK5AD, anti-KDM5A/D siRNA; siK5CD, anti-KDM5C/D siRNA; siK5A, anti-KDM5A siRNA; siK5B, anti-KDM5B siRNA; siK5C, anti-KDM5C siRNA; and siK5D, anti-KDM5D siRNA. In (A), (B), and (F) statistical significance was compared with OSKM-treated fibroblasts, whereas in (C) it was compared with DMSO (0.1%) treatment using two-way ANOVA and a post-hoc Tukey test. Data are represented as mean ± SD. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.