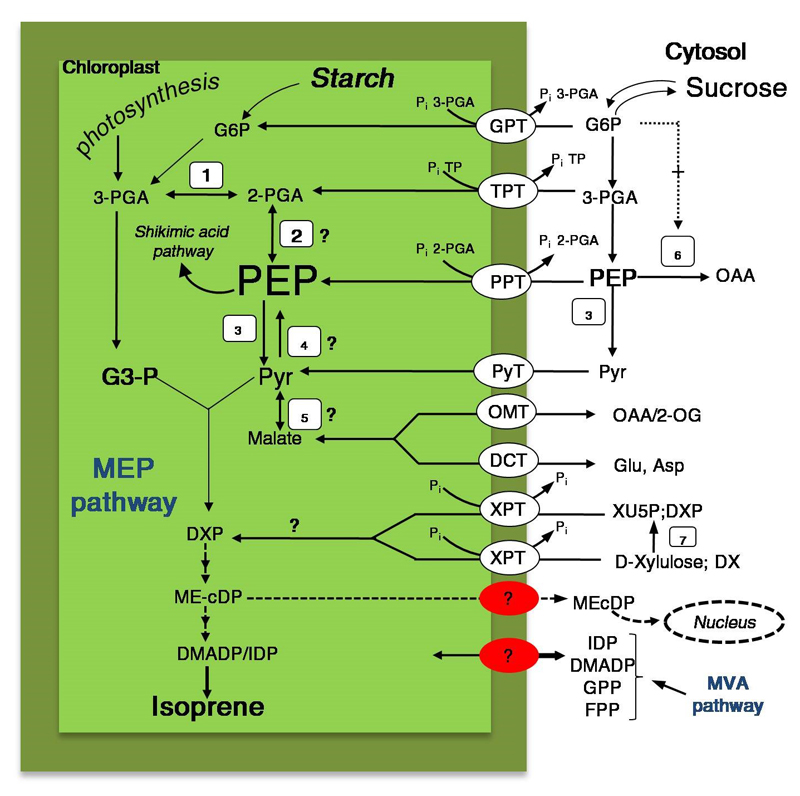
Figure 2.
A review of the current understanding of chloroplastic phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) synthesis associated with pyruvate formation and specific transporters that mediate the transport of intermediates through the plastid membrane. The primary products of photosynthesis, triose phosphates, are exported via the triose phosphate/phosphate translocator (TPT), or metabolized in chloroplasts. The PEP, can be imported via PEP/phosphate translocator (PPT), or synthetized by plastidic enolase (2) or, to a lesser extent, by the pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase (4) enzyme. PEP in the chloroplasts can enter the shikimic acid pathway or, after pyruvate (Pyr) formation, enter the MEP pathway. There are several possible sources for Pyr inside the chloroplasts: 1) export of cytosolic PEP through a PEP/phosphate translocator (PPT) [107] and its conversion to pyruvate via glycolysis involving phosphoglycerate mutase (PGL) and enolase (ENO) [148]; 2) synthesis from PEP by pyruvate kinase (PK) [149]; 3) via NADP-dependent malate dehydrogenase within chloroplast [150,151]; or 4) import from the cytosol via plastid Na+-coupled pyruvate transporter (PyT) [152]. The malate can be transported across the plastid inner envelope membrane through the so-called malate valve (or malate shunt) facilitated by 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG)-malate transporter (OMT) or via plastidial dicarboxylate transporter (DCT), which acts as an antiporter exchanging malate against glutamate (Glu) and aspartate (Asp) [119,151,153]. The product of starch and sucrose degradation, glucose 6-phosphate (G6P), is imported into the chloroplast by a hexose translocator (GPT). This specific metabolite is considered to be a positive allosteric effector of the PEP carboxylase enzyme (6). The figure shows a possible traffic of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (ME-cDP) from plastid into cytosol and its transfer to the nucleus. In addition, pentose intermediates, D-xylulose and 1-deoxy-D-xylulose (DX), can be phosphorylated to and/or subsequently translocated into the MEP pathway from xylulose 5-phosphate (XPT) carrier. Metabolites: DXP, 1-Deoxy-D xylulose 5-phosphate; XU5P, xylulose 5-phosphate. Enzymes numbering: phosphoglycerate mutase (1); enolase (2); pyruvate kinase (3); pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase (4); NADP-malate dehydrogenase (5); PEP carboxylase (6); xylulose kinase (7). The questions marks indicate steps for which the enzymes involved in isoprenoid metabolism or transport activities (red circles) remain to be elucidated.