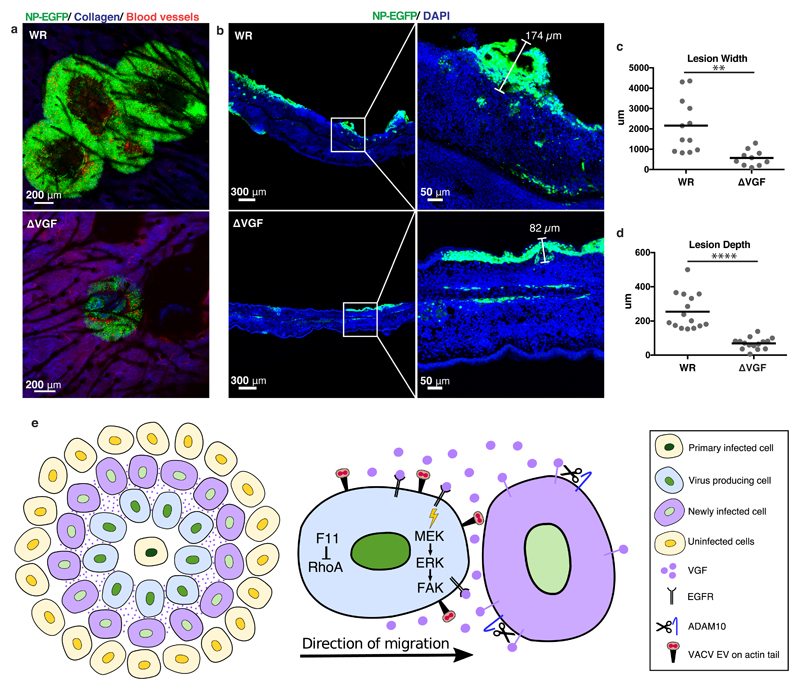
Figure 4. VGF is required for lesion formation in vivo.
a, Multiphoton microscopy of WR and ΔVGF lesions in mice ear pinnae 6 days pi. Infected cells (green), collagen (blue), blood vessels (red). b, Confocal imaging of WR and ΔVGF lesions in cross section. Infected cells (green), nuclei (blue) c, d Quantification of lesion widths and depths from a and b, respectively. e, Model of VGF mediated VACV induced cell motility (refer to text for details). Representative data from 2 mice/virus in biological triplicates (a. b). Lines represent means of 10-15 lesions per condition from 5 mice/virus (3 cross-section, 2 frontal sections). Unpaired t-test was applied (**** P< 0.0001, ** P< 0.01) (c, d). See Supplementary Table 1 for exact statistics.