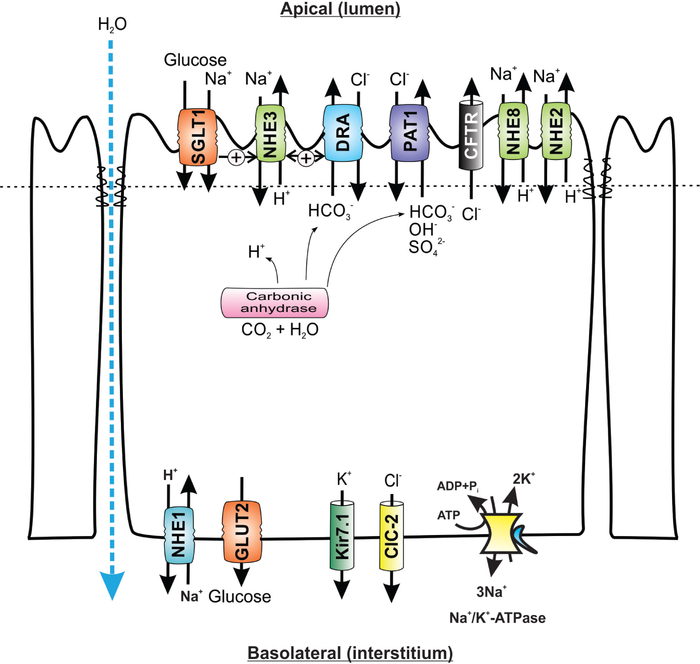
Figure 3.
Simplified cellular model of the role of apical Na+/H+ exchange in transepithelial sodium, glucose, and water absorption in small intestinal epithelial cells. SGLT1, sodium/glucose cotransporter 1, SLC5A1; GLUT2, glucose transporter 2, SLC2A2; DRA, downregulated in adenoma, SLC26A3; PAT1, putative anion transporter 1, SLC26A6; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, Kir7.1, potassium inwardly rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 13, KCNJ13; ClC-2, chloride channel protein 2, CLCN2. For detailed reviews about the physiology and pathophysiology of intestinal electrolyte transport and Na+/H+ exchange in particular, see Fuster and Alexander (93), He and Yun (115), Zachos et al. (339), and Gurney et al. (109)