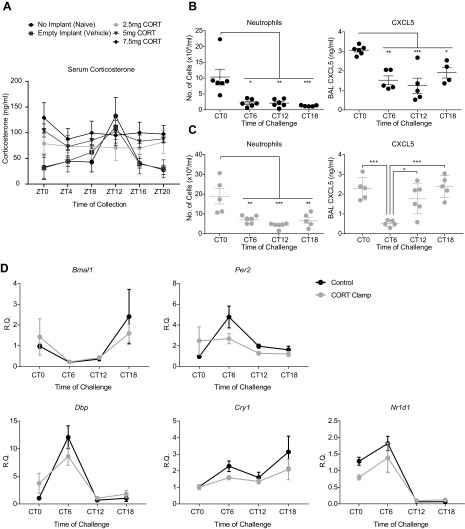
Figure 1.
Time-of-day variation in pulmonary LPS response is retained despite corticosterone clamp. A) Dose–responses used to establish optimal corticosterone (CORT) clamp concentration. Corticosterone concentration in serum samples from tail blood taken at the indicated time points, n = 5–7. Analysis was performed by 2-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test between time points, and a significant main effect of treatment was observed. Individual dose plots are shown in Supplemental Fig. 2; a dose of 2.5 mg was used in subsequent experiments. B, C) Inflammatory measurements 5 h after nebulized LPS exposure at the indicated time points. Neutrophil counts in BAL fluid and BAL CXCL5 concentration in control animals (B) and CORT-clamped animals (C), median age 12 wk, n = 4–6/group. Analysis using Grubbs’ test revealed 3 outliers in the CXCL5 results in C (1 each from CT0, CT6, and CT18), which were removed before further analysis. Analysis was performed by 1-way ANOVA and post hoc tests with Tukey’s correction. Asterisk denotes significance from CT0 time point, except where indicated. D) mRNA expression of a panel of clock genes in whole lung of CORT-clamped and control animals after LPS challenge. Analysis was performed via 2-way ANOVA; all genes showed a significant effect of time but no differences between treatments. Data represent means ± se. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.