Figure 1.
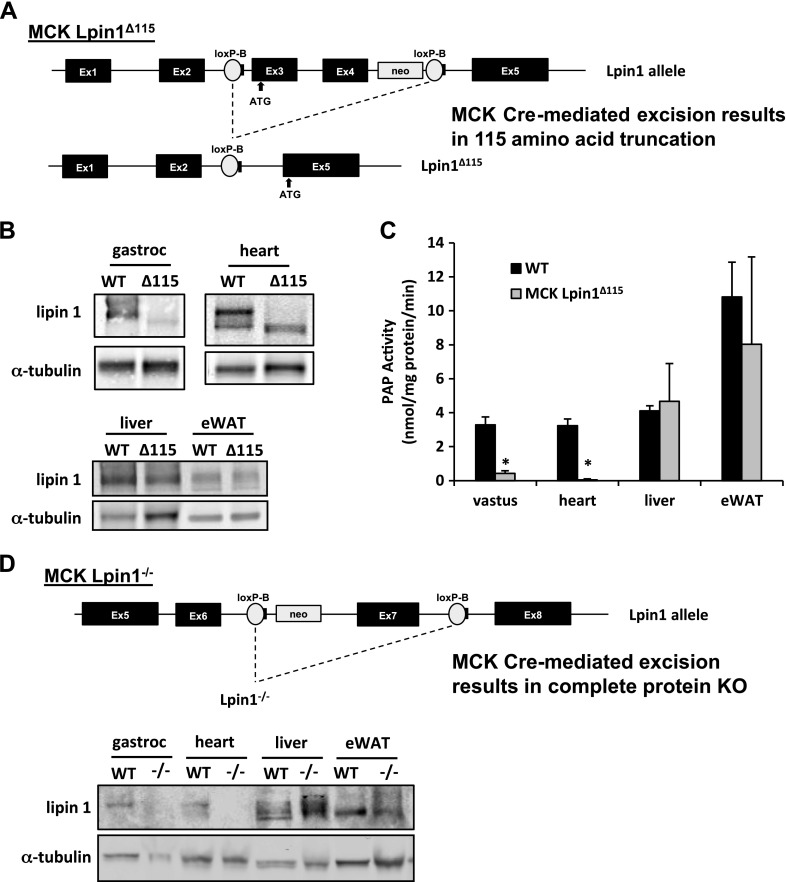
Generation of mouse models with muscle-specific lipin 1 deficiency. A) Schematic showing Lpin1 gene-targeting strategy for generation of truncated lipin 1. MCK-Lpin1Δ115 animals were generated using LoxP sites flanking exons 3 and 4 of lipin 1, which encode the principal start codon. MCK-driven Cre recombination led to enforcement of an alternative start codon in exon 5. B) Western blot analysis of gastrocnemius, heart, liver, and eWAT from WT and MCK-Lpin1Δ115 mice. C) PAP activity in vastus, heart, liver, and eWAT of WT and MCK-Lpin1Δ115 mice. Data are shown as means ± sem. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t test) for differences in MCK-Lpin1Δ115 compared with WT mice. n = 5–6 and animals were 3–4 mo old. D) Schematic showing Lpin1 gene-targeting strategy for generation of full-protein knockout of lipin 1. MCK-Lpin1−/− animals were generated with LoxP sites flanking exon 7 of lipin 1, and MCK-driven Cre recombination led to complete ablation of the lipin 1 protein. Western blot analysis of gastrocnemius, heart, liver, and eWAT from WT and MCK-Lpin1−/− mice 3–4 mo old; n = 5.