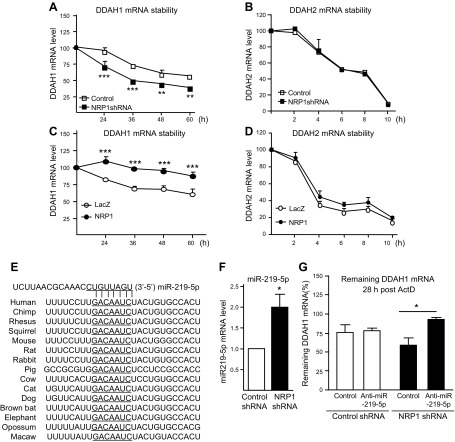
Figure 2.
NRP1 controls mRNA stability of DDAH1 via miR-219-5p in endothelial cells. A–D) mRNA stability of DDAH1 and DDAH2 was quantified with qPCR in NRP1 knockdown HUVECs (A, B) and NRP1 overexpressing HUVECs (C, D) after administration with actinomycin D (ActD; 5 μg/ml) (n = 4 for each group). E) Sequence alignment of the miR-219-5p base-pairing sites in the 3′-untranslated region of DDAH1 mRNAs, which are highly conserved among human, chimpanzee, rhesus monkey, squirrel, mouse, rat, rabbit, pig, and cow, among others. The “seed” sequences of miR-219-5p complementary to DDAH1 are underlined. F) The miR-219-5p mRNA level was validated in NRP1 knockdown HUVECs with qPCR (n = 7 for each group). G) Control HUVECs and NRP1 knockdown HUVECs were transfected with an miR219-5p inhibitor or corresponding control, and then administered ActD (5 μg/ml). mRNA was collected at time 0 and 28 h post-ActD administration, and mRNA stability of DDAH1 was examined (n = 4 for each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.